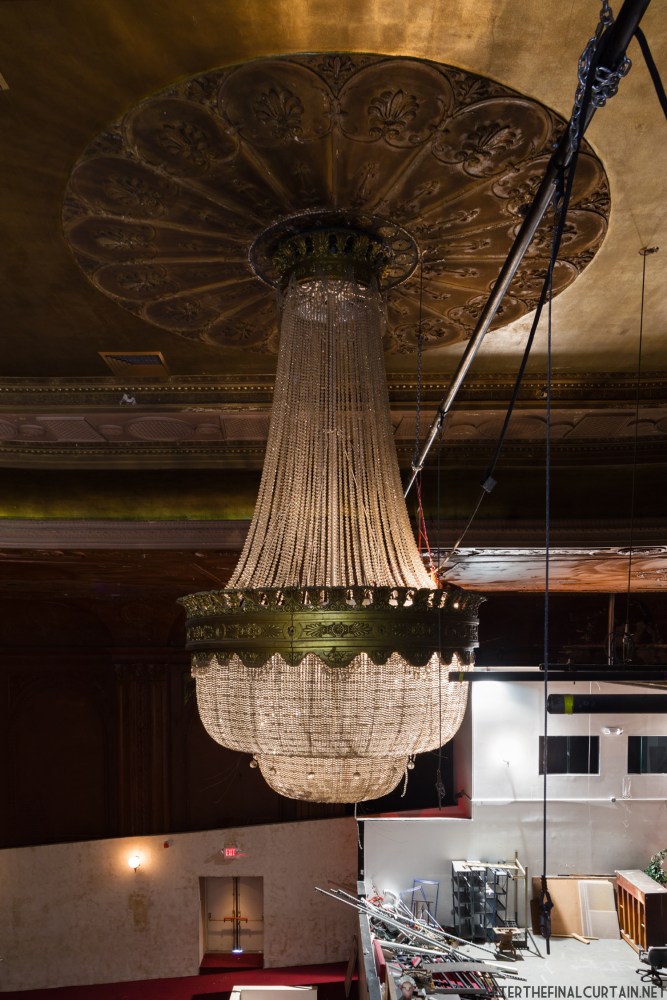
This was originally posted on After the Final Curtain’s Patreon in November 2022. For expanded early posts, as well as video walkthroughs and other exclusive content, you can become a patron at: https://www.patreon.com/afterthefinalcurtain
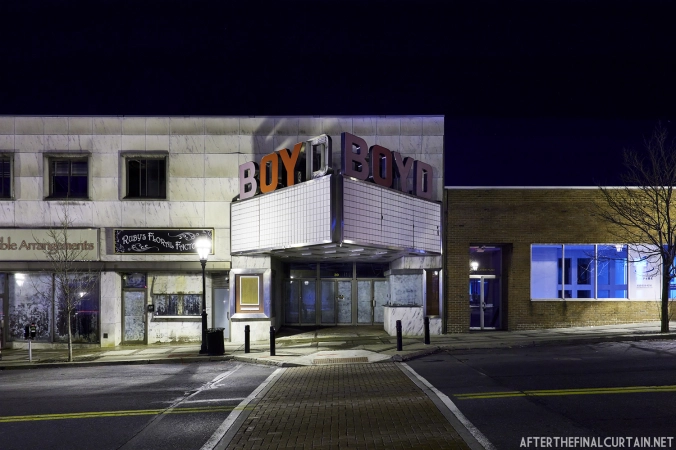
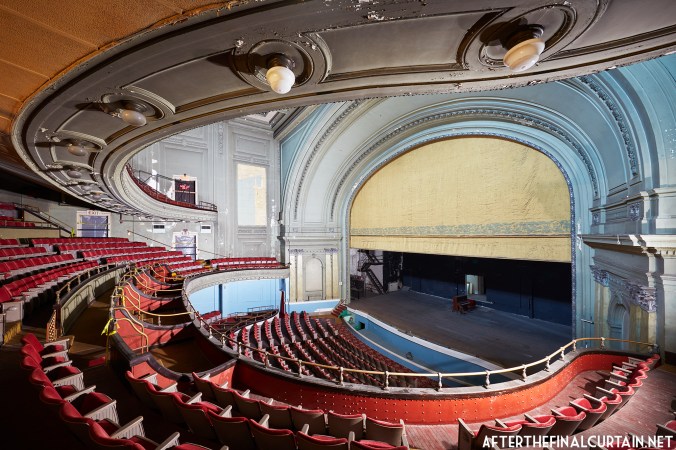
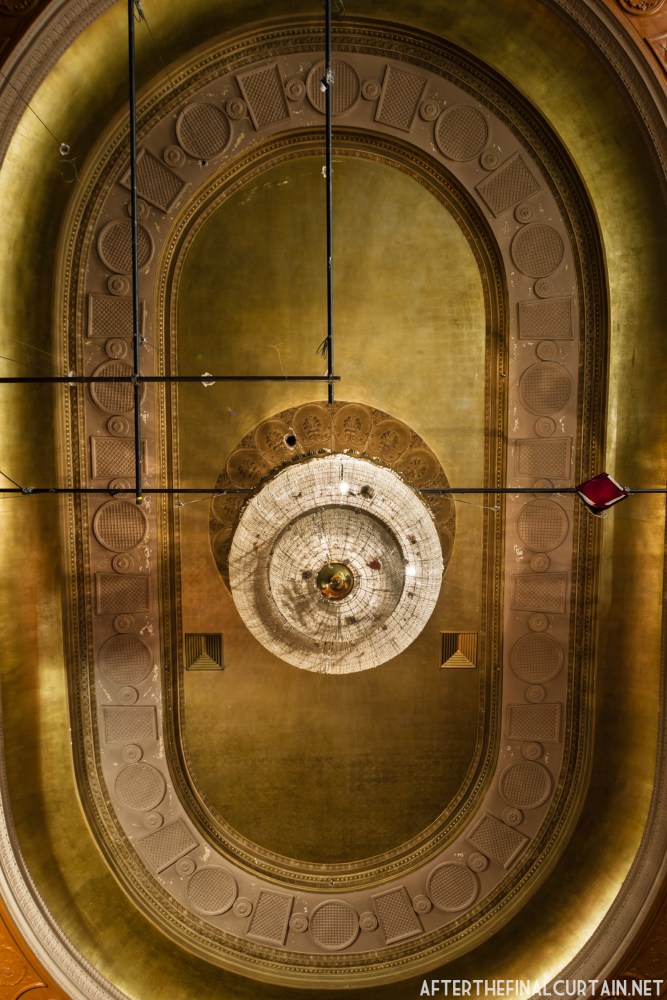
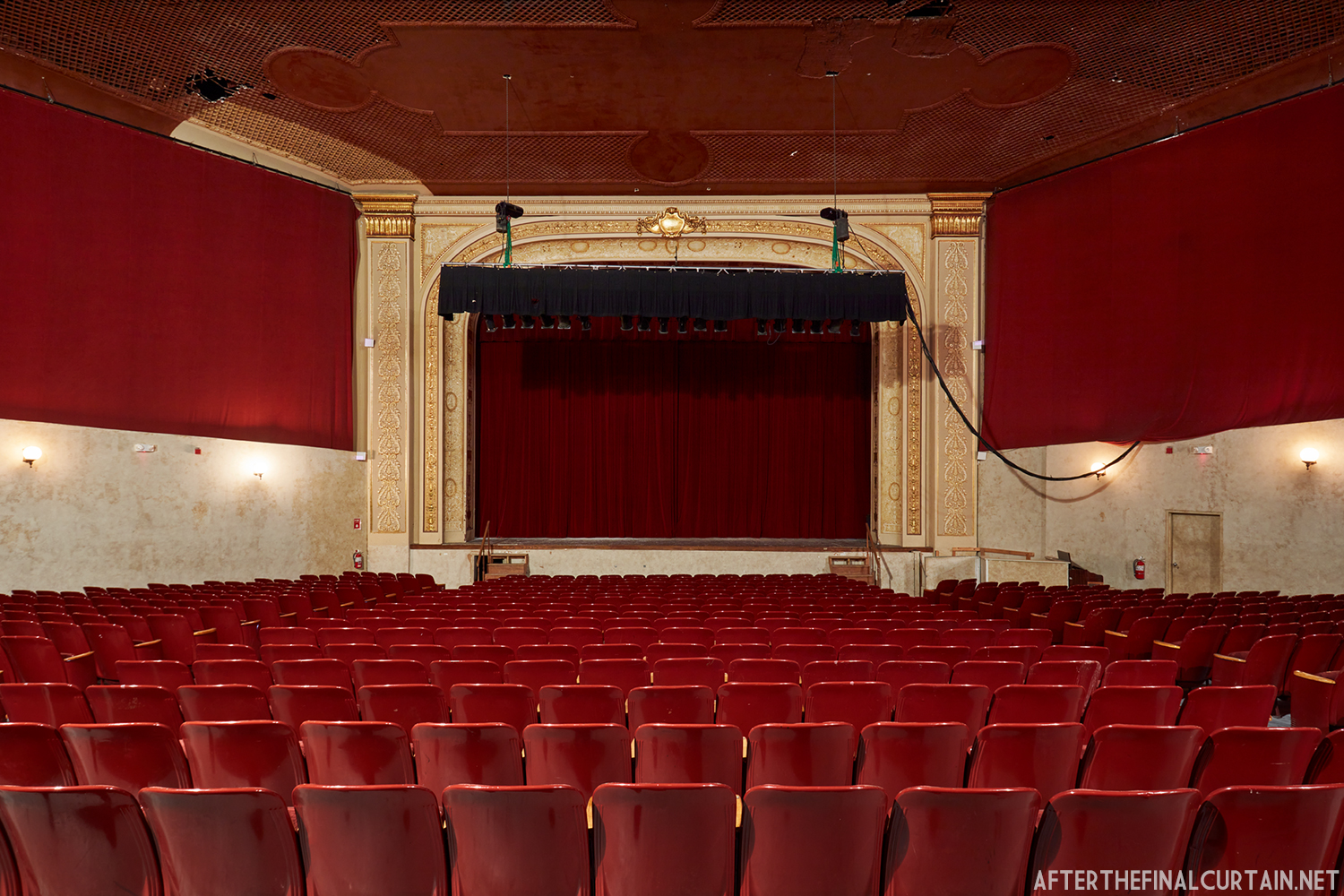
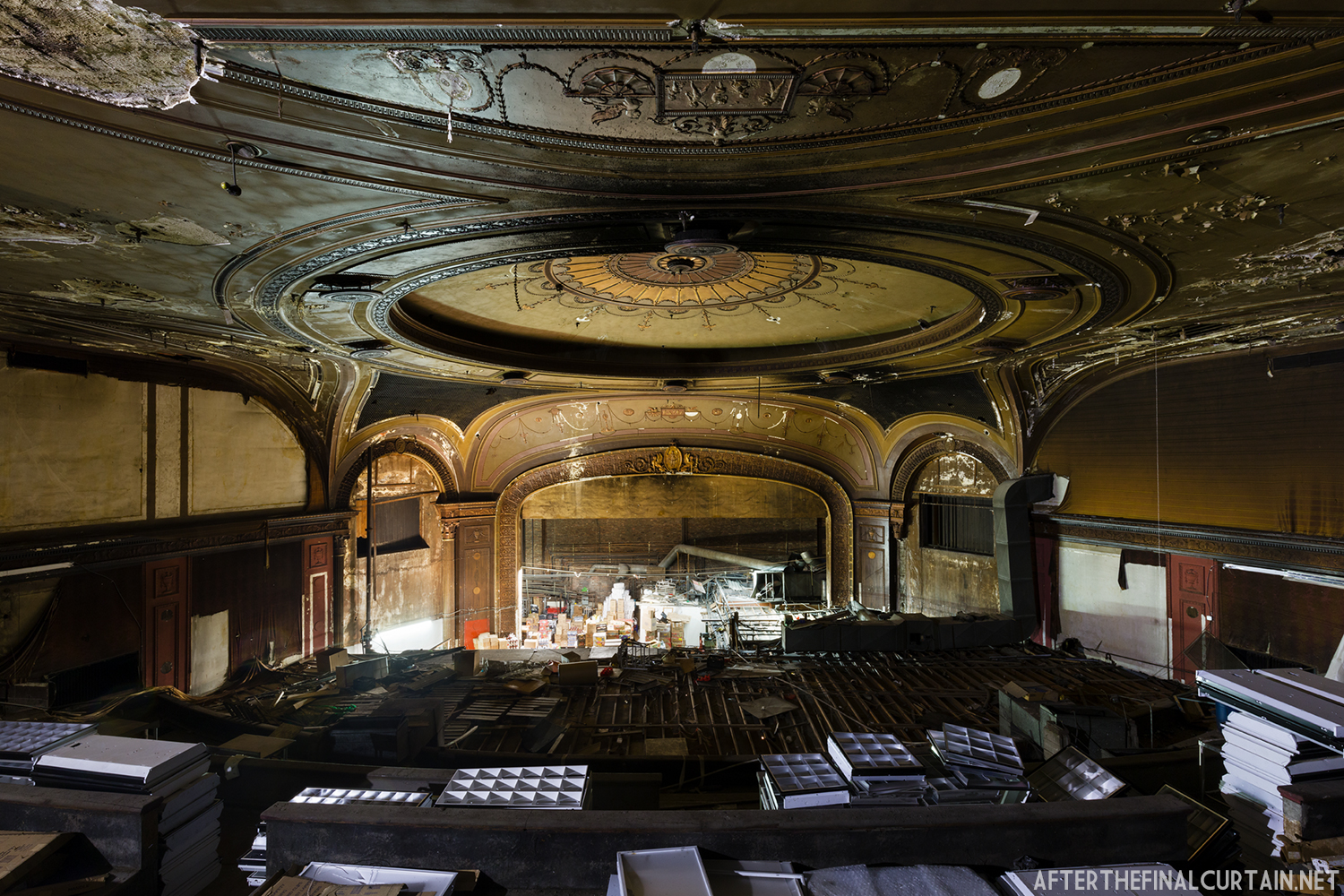
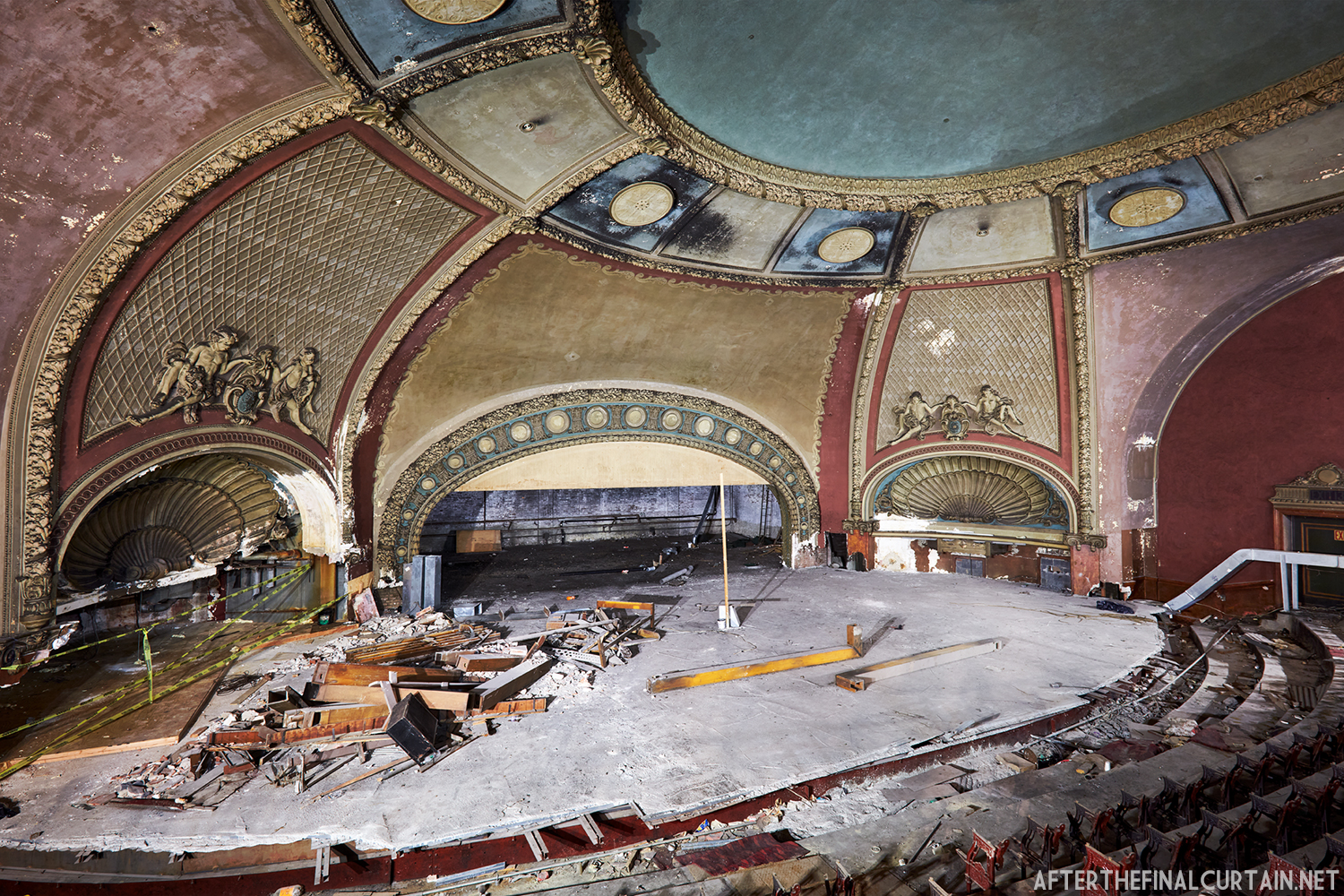
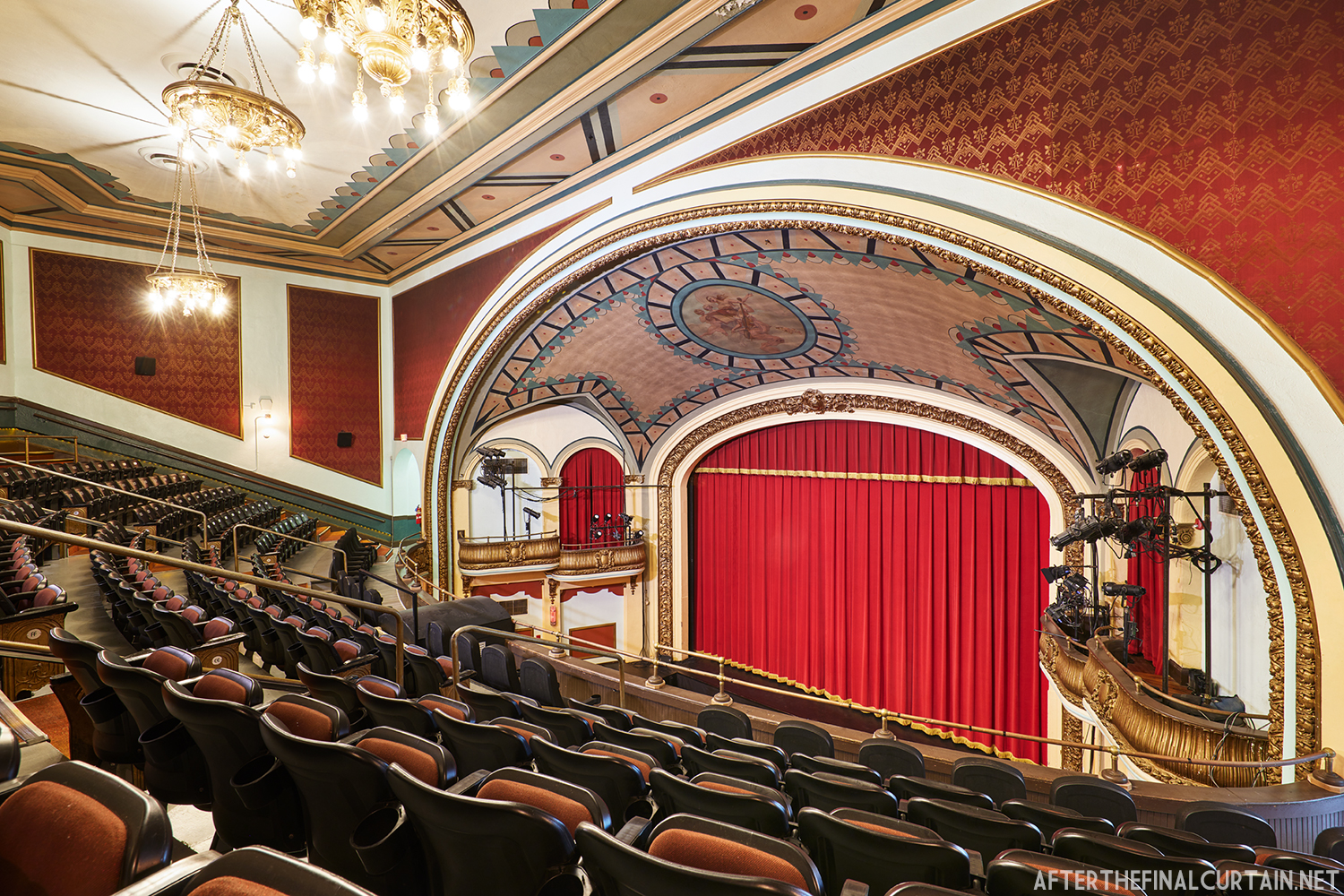
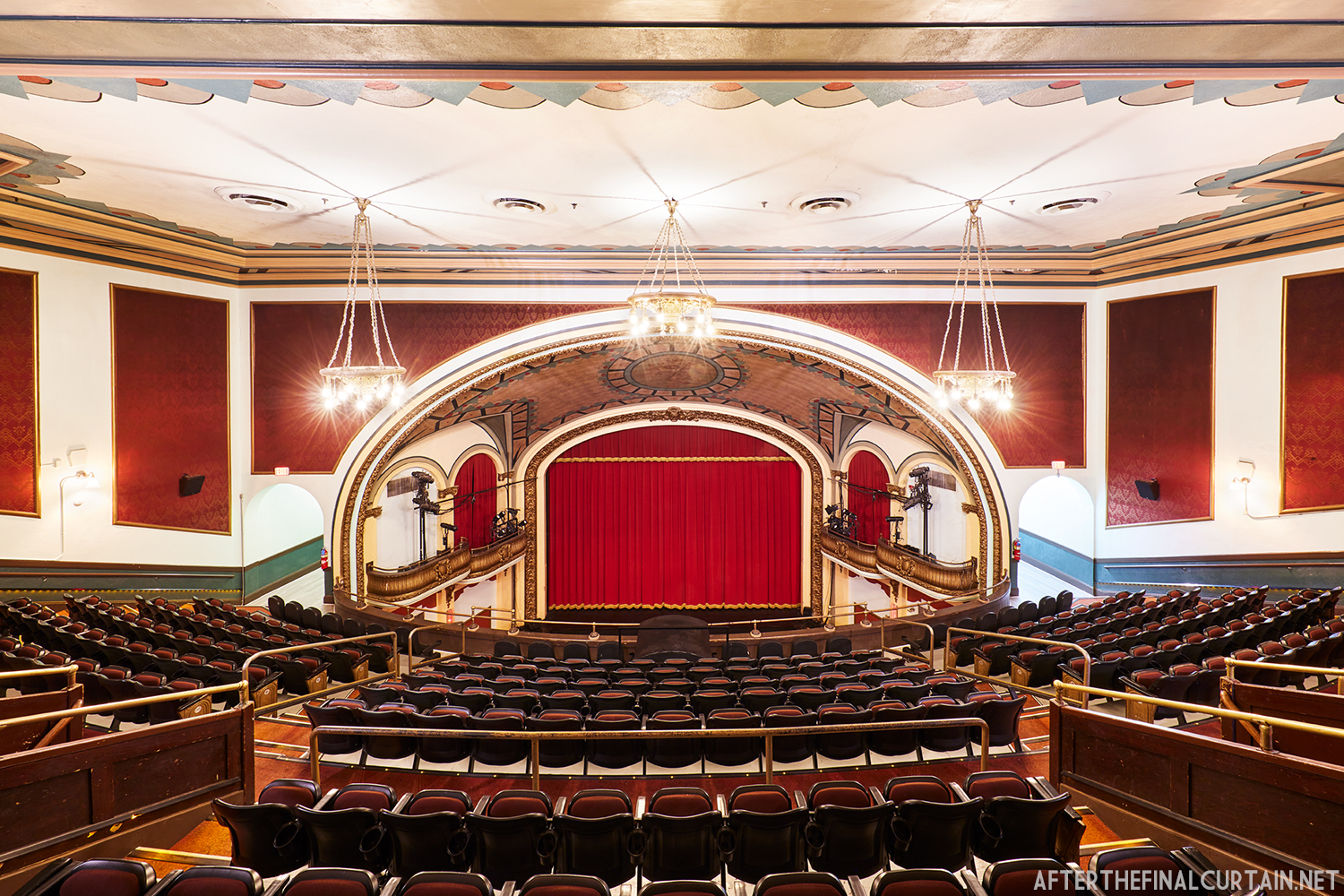
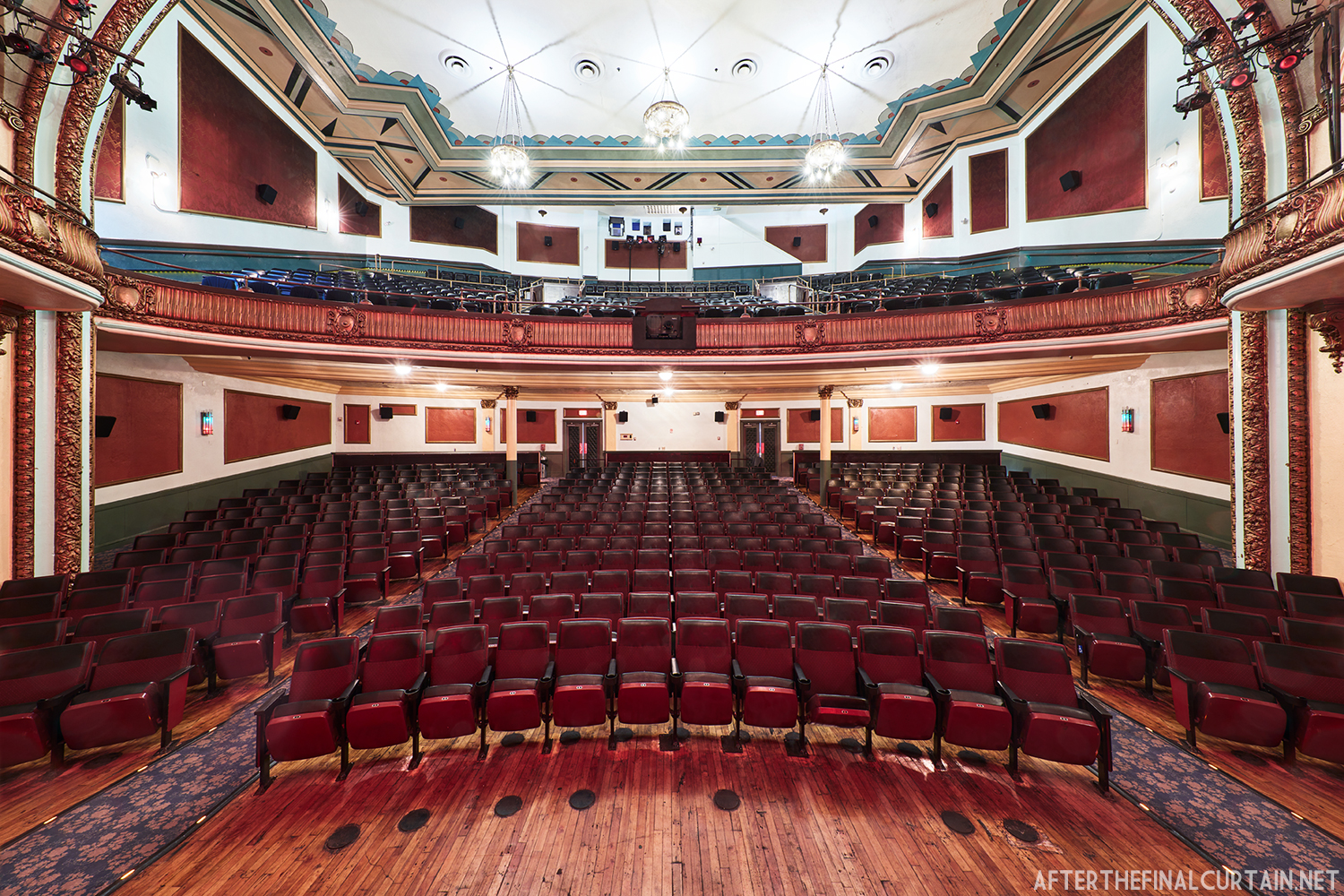
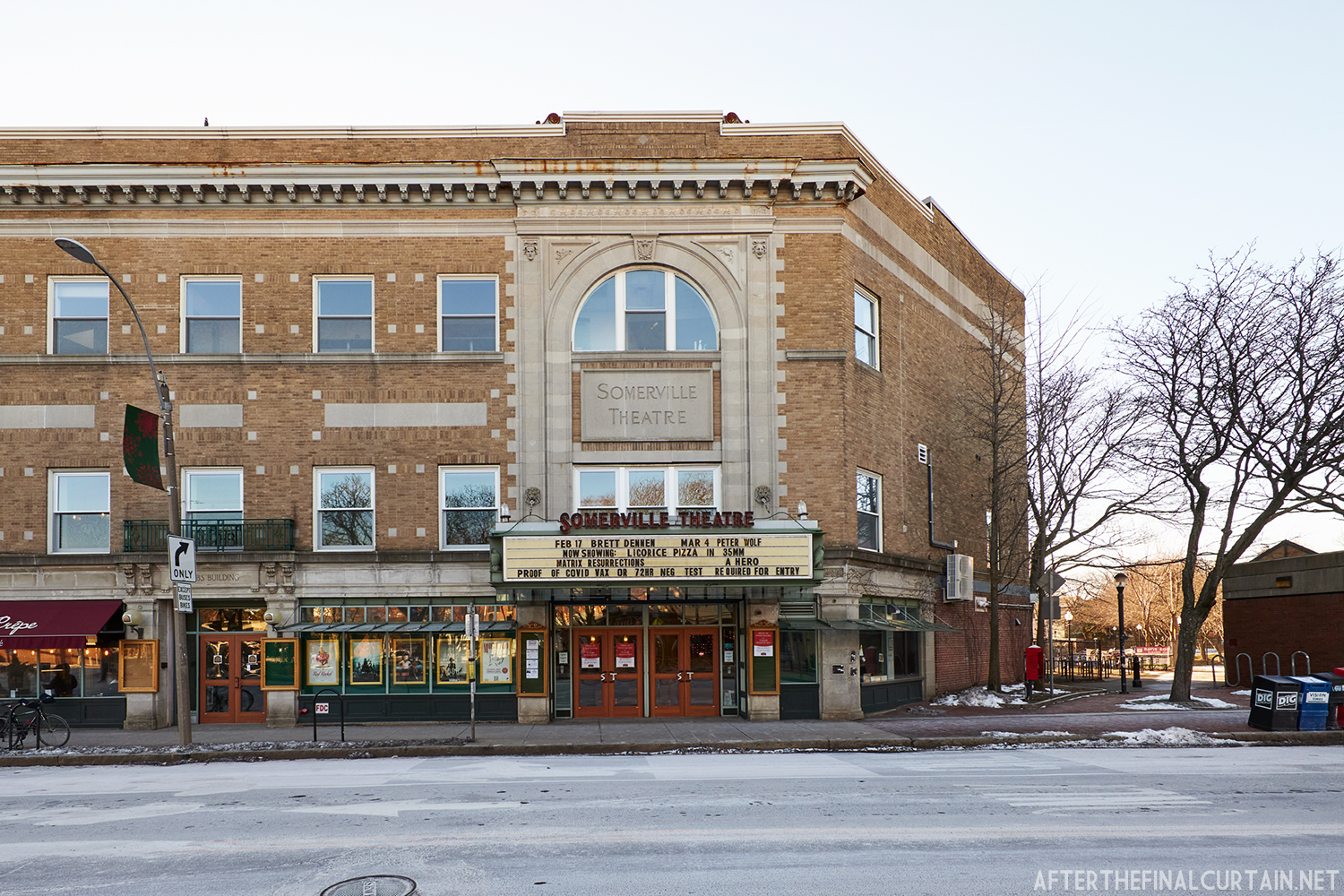
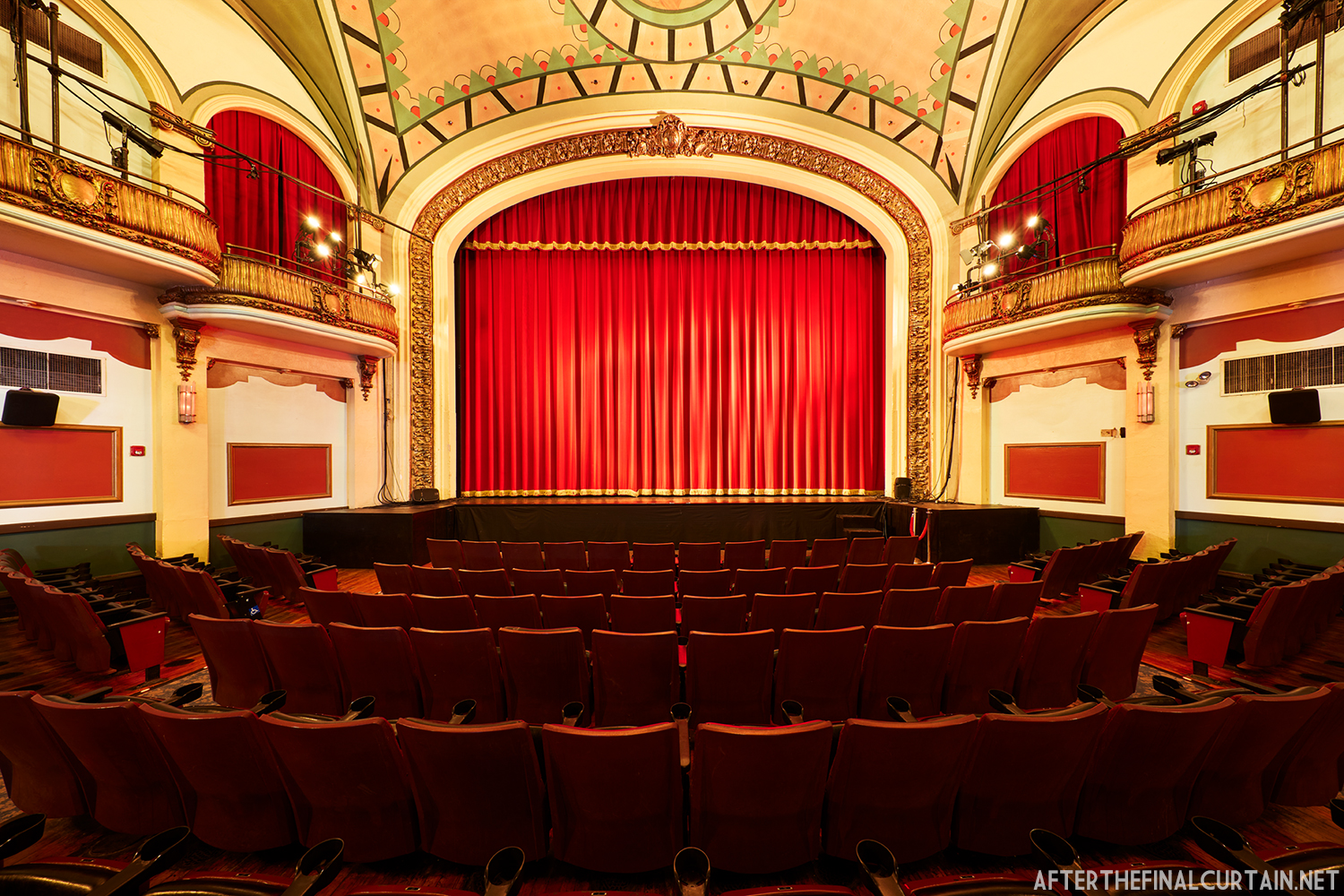
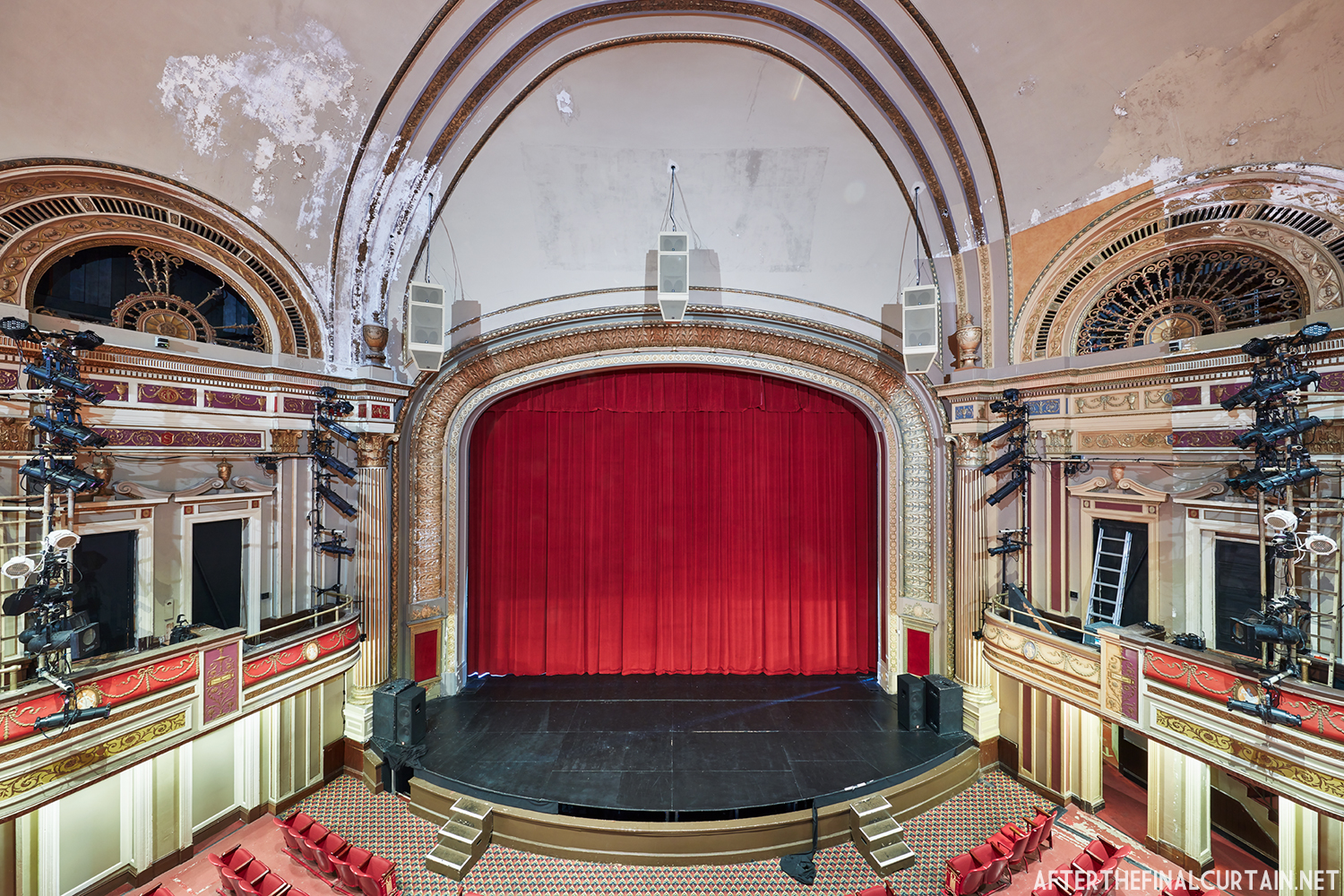
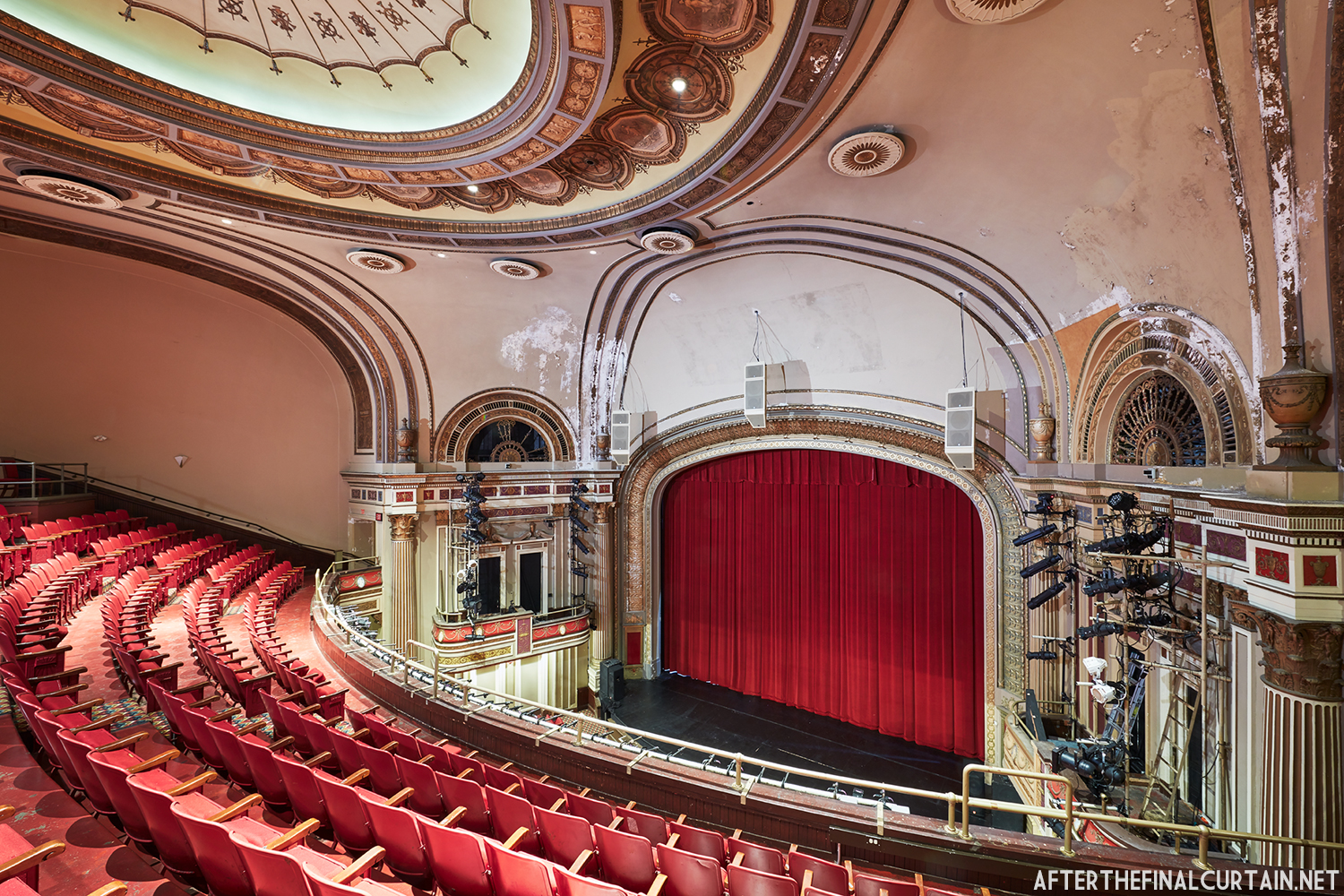
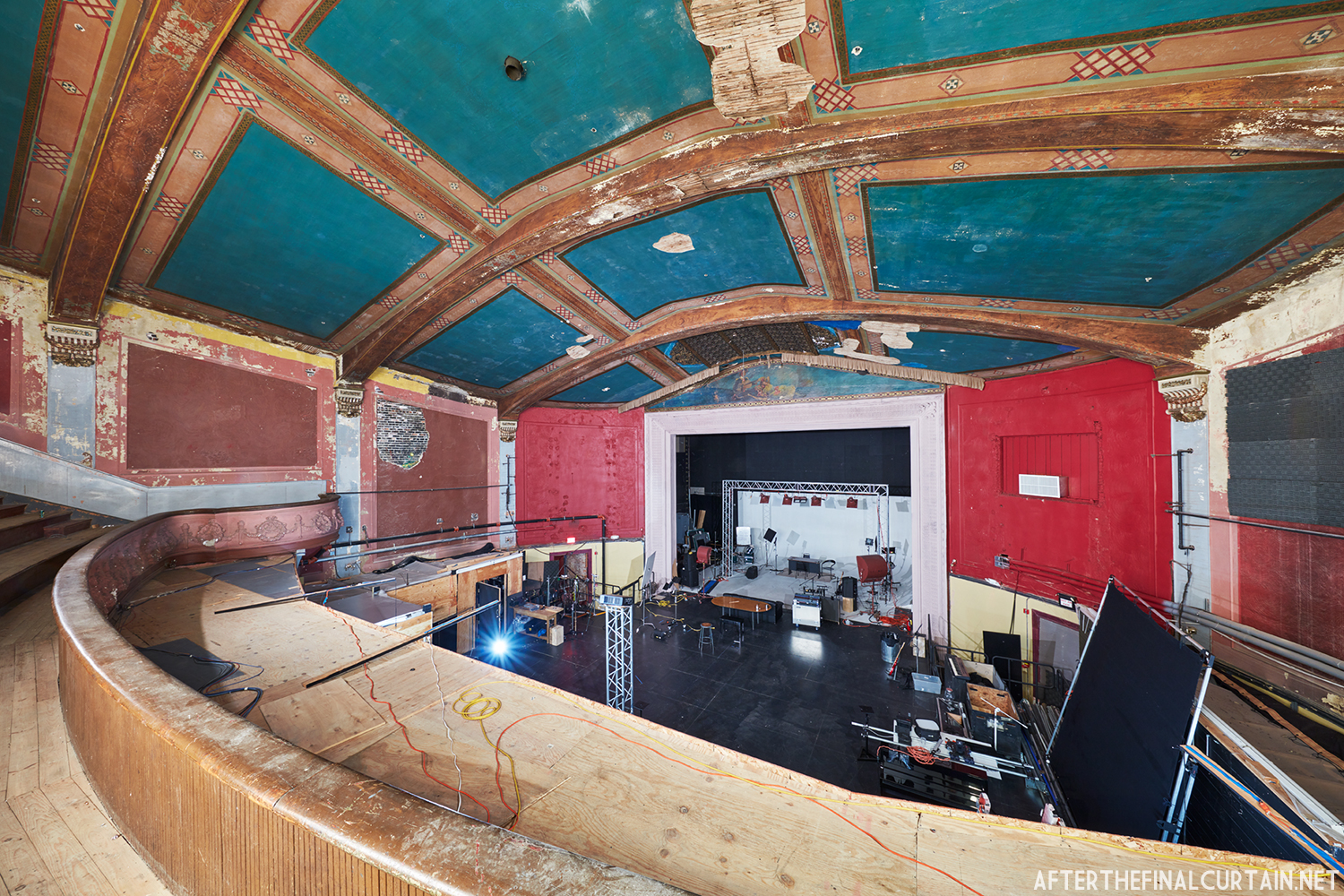
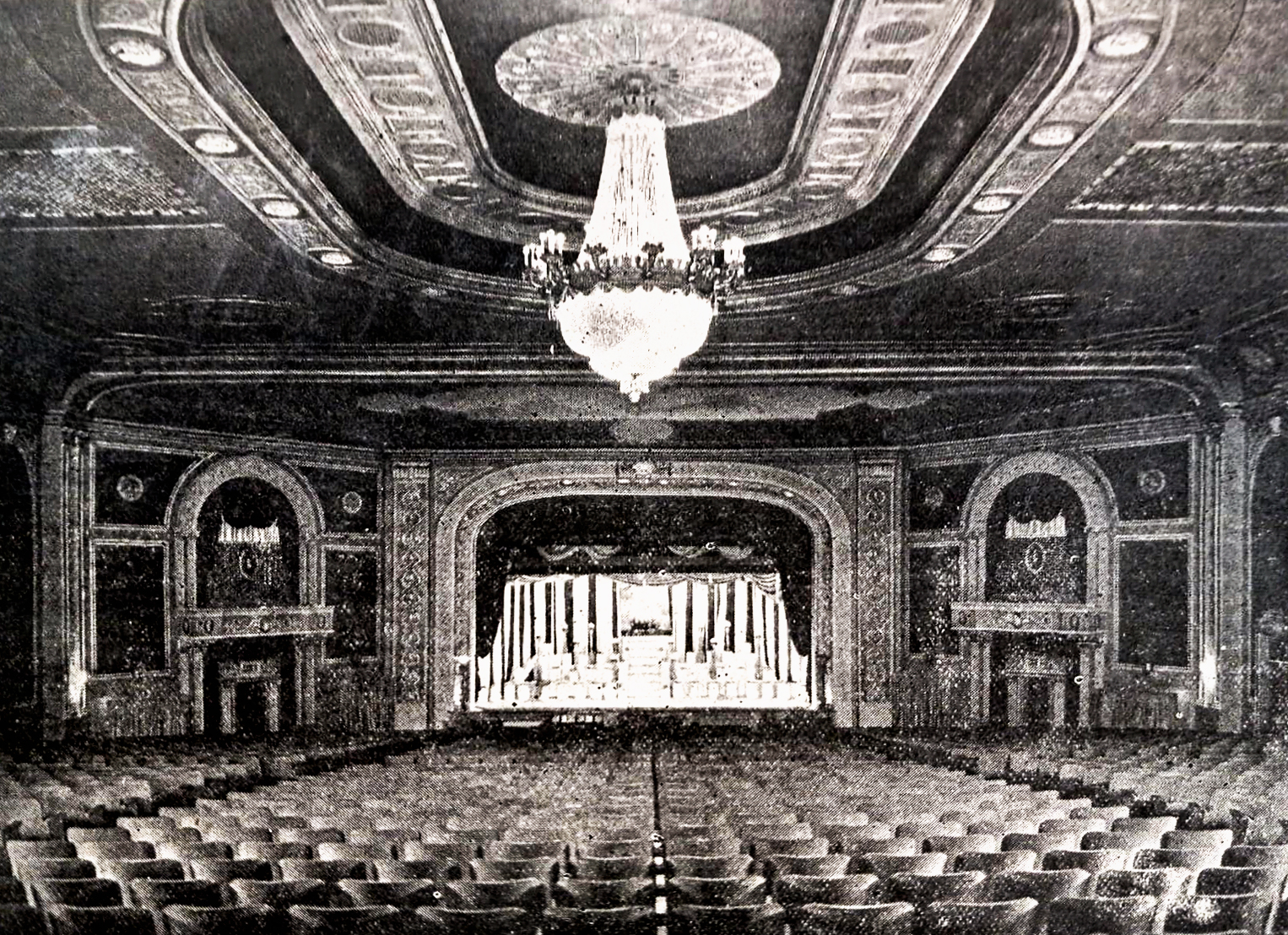
Built at a cost of $250,000 ($4.1 million when adjusted for inflation) The Boyd Theatre in Bethlehem, PA originally opened on September 1, 1921 as the Kurtz Theatre. It was designed by E. C Horn Sons of New York City for Charles and John Kurtz, in the streamline moderne architectural style. The 1,626 seat theater originally featured vaudeville and silent films as part of the Shubert Advance Vaudeville circuit.
Opening night featured a performance from a seven-piece orchestra, a minstrel show, two vaudeville acts, the silent film “The Great Moment” starring Gloria Swanson, and the theater organist playing the Estey pipe organ. Less than two months after opening, on October 24, 1921, the theater discontinued vaudeville, and began only showing silent films. The first film shown after this change was “Way Down East” starring Lillian Gish. In October 1922, the Broadway Players, a comedic opera company, began holding performances at the theater. In 1924, E.C. Horn Sons sued the Kurtz Brothers for non-payment of fees for their part in constructing the theater. They were awarded $21,000, or $364,000 with inflation, later that year.
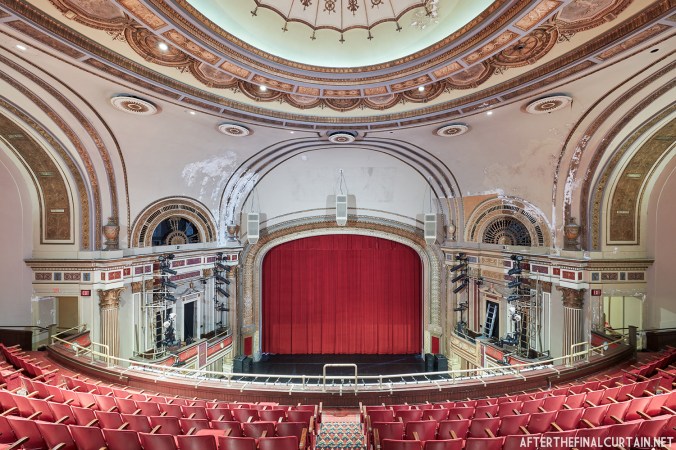
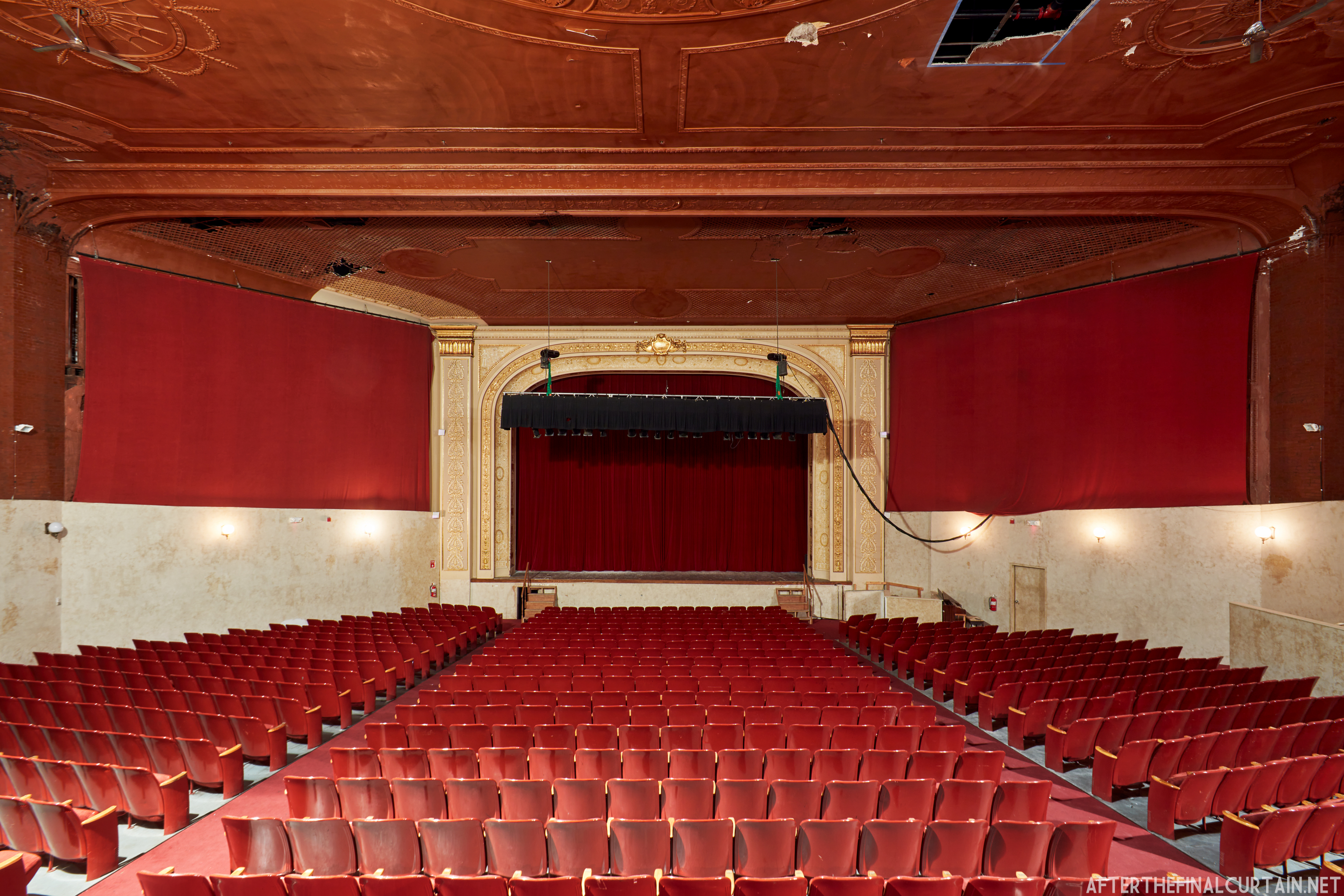
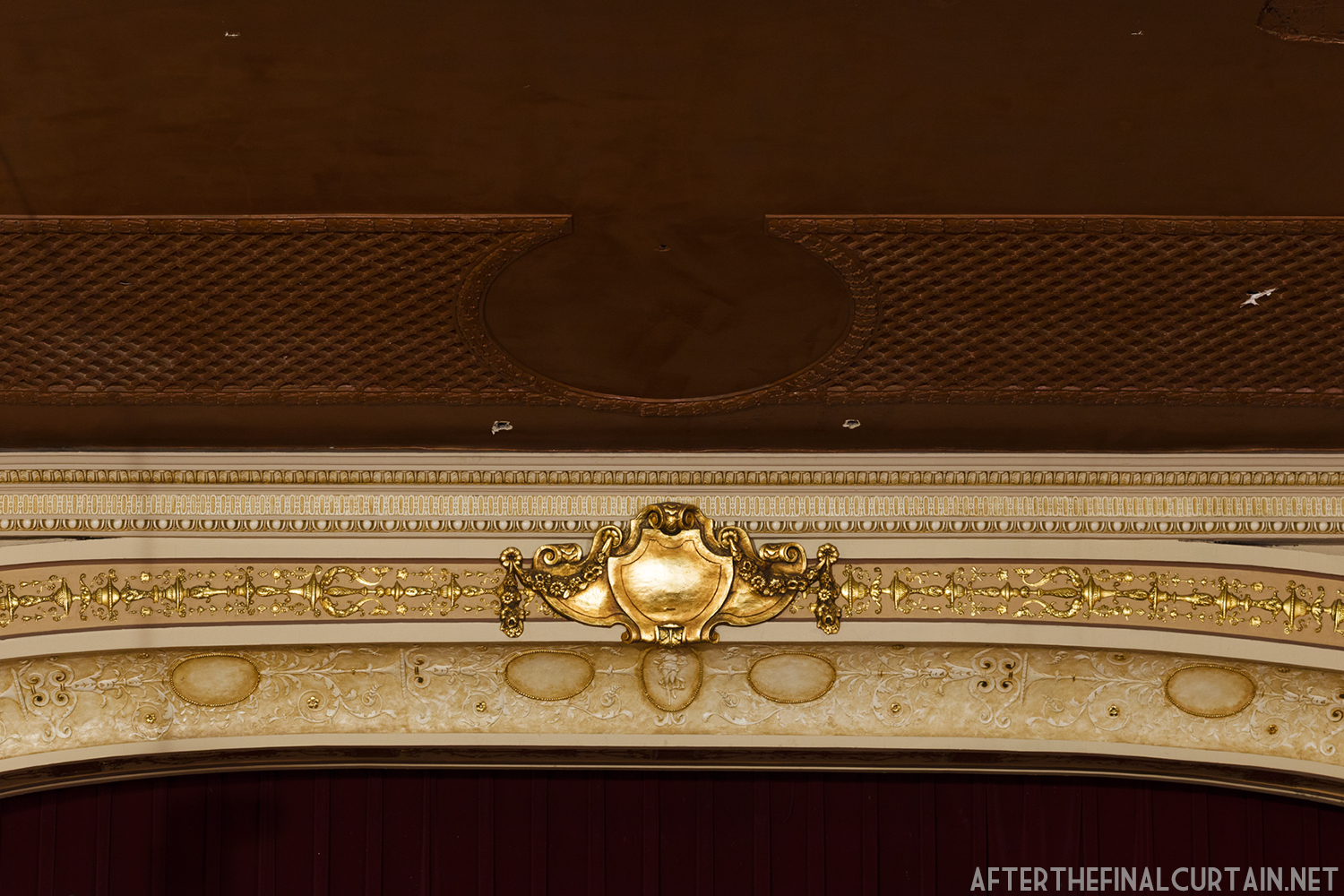
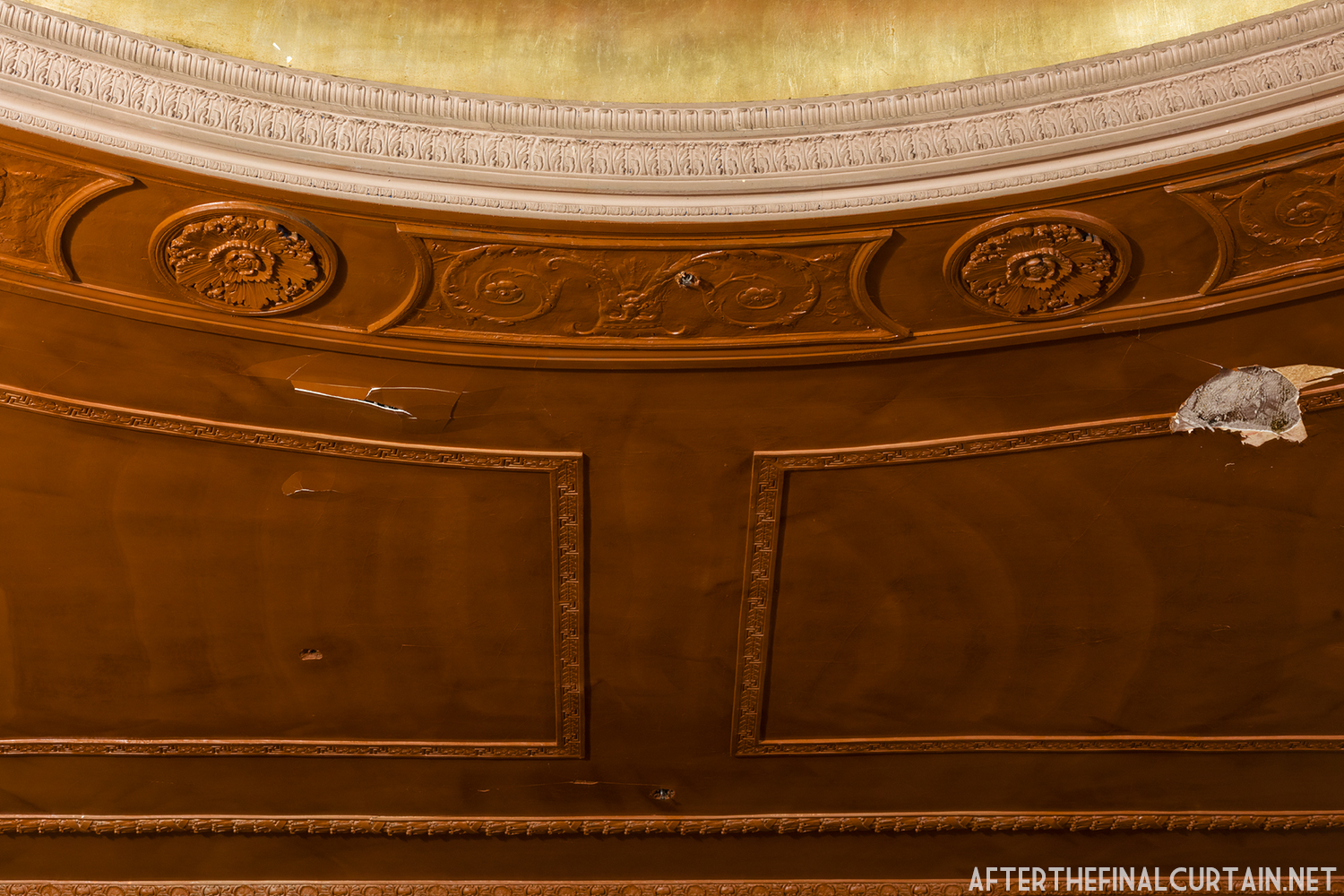
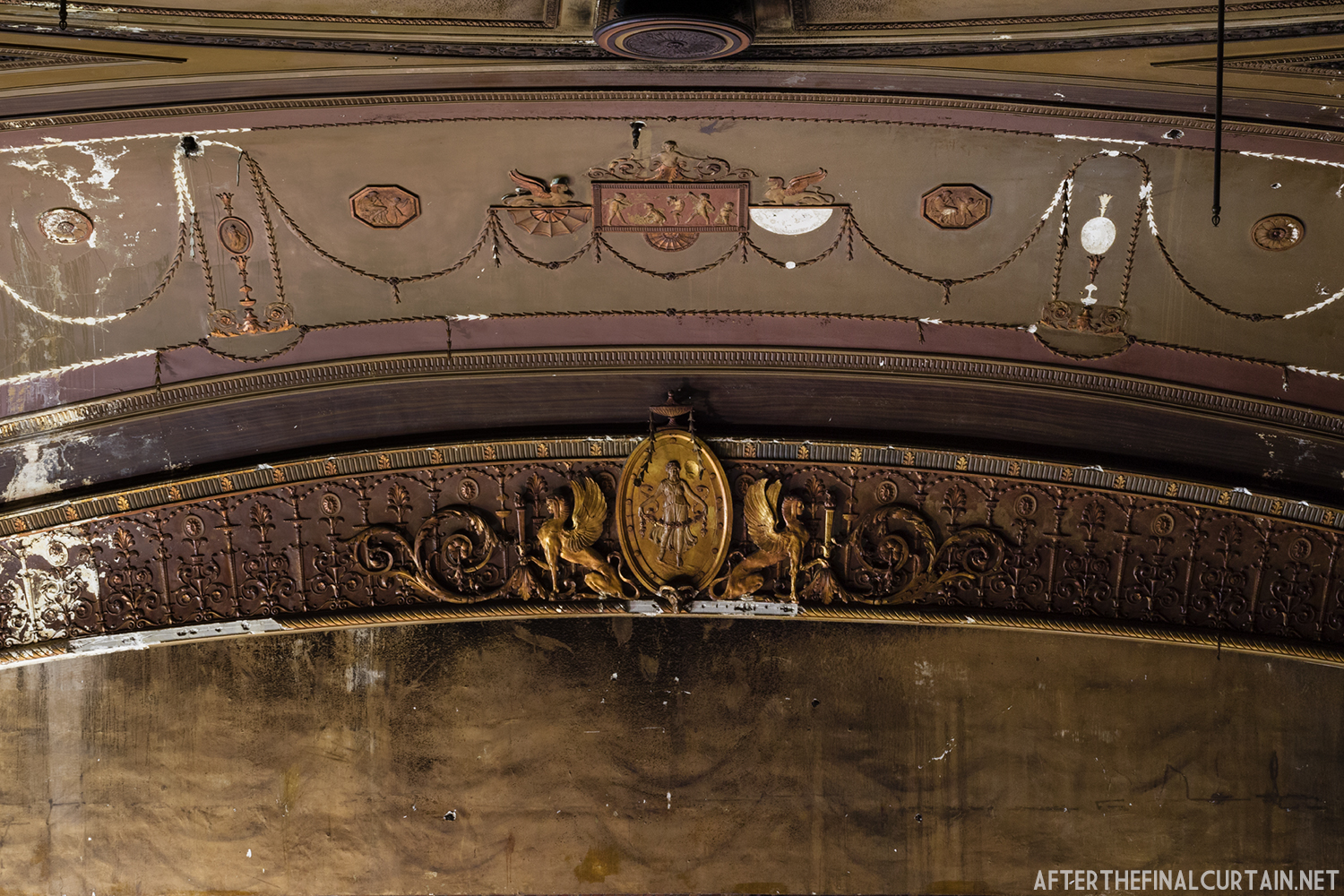
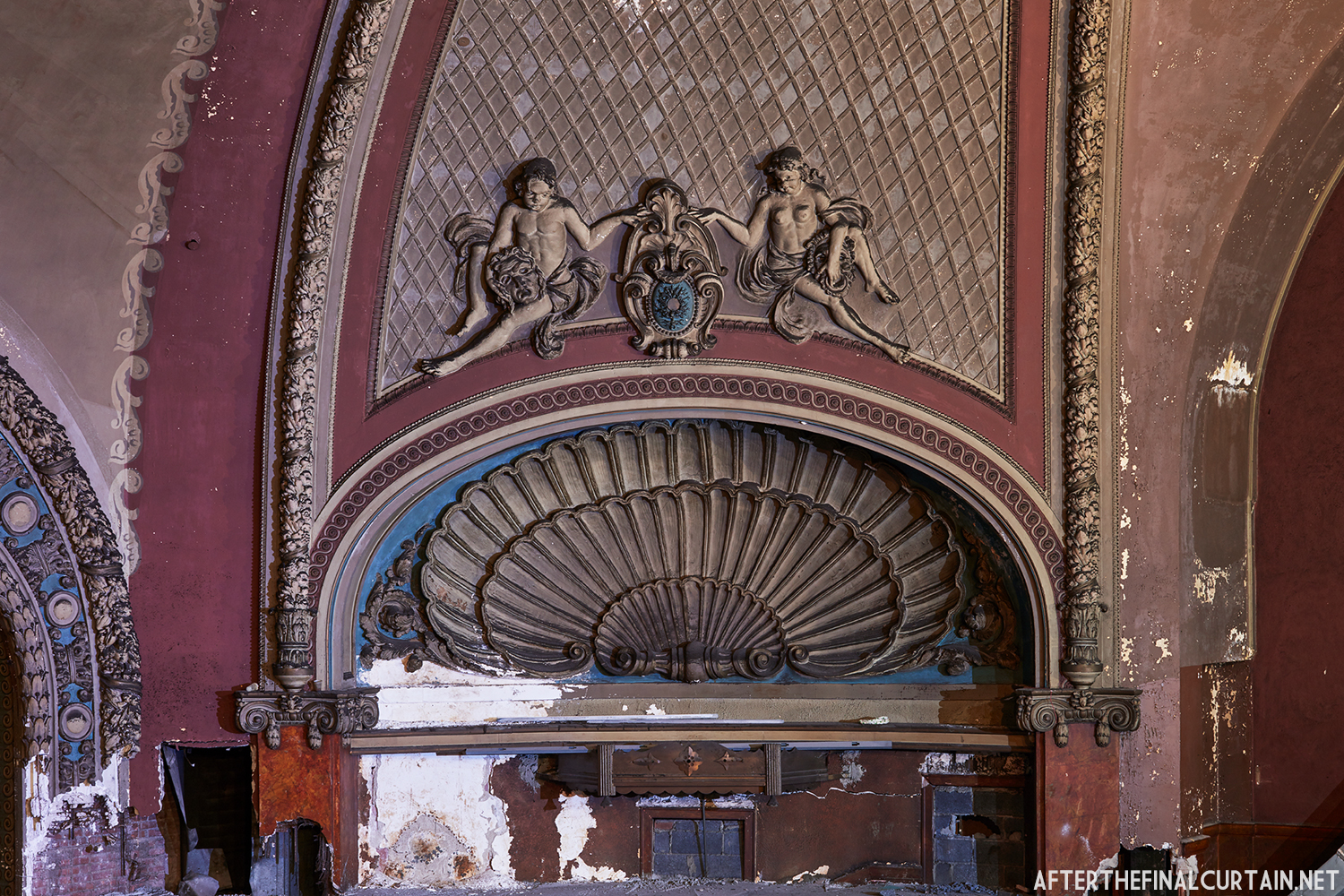
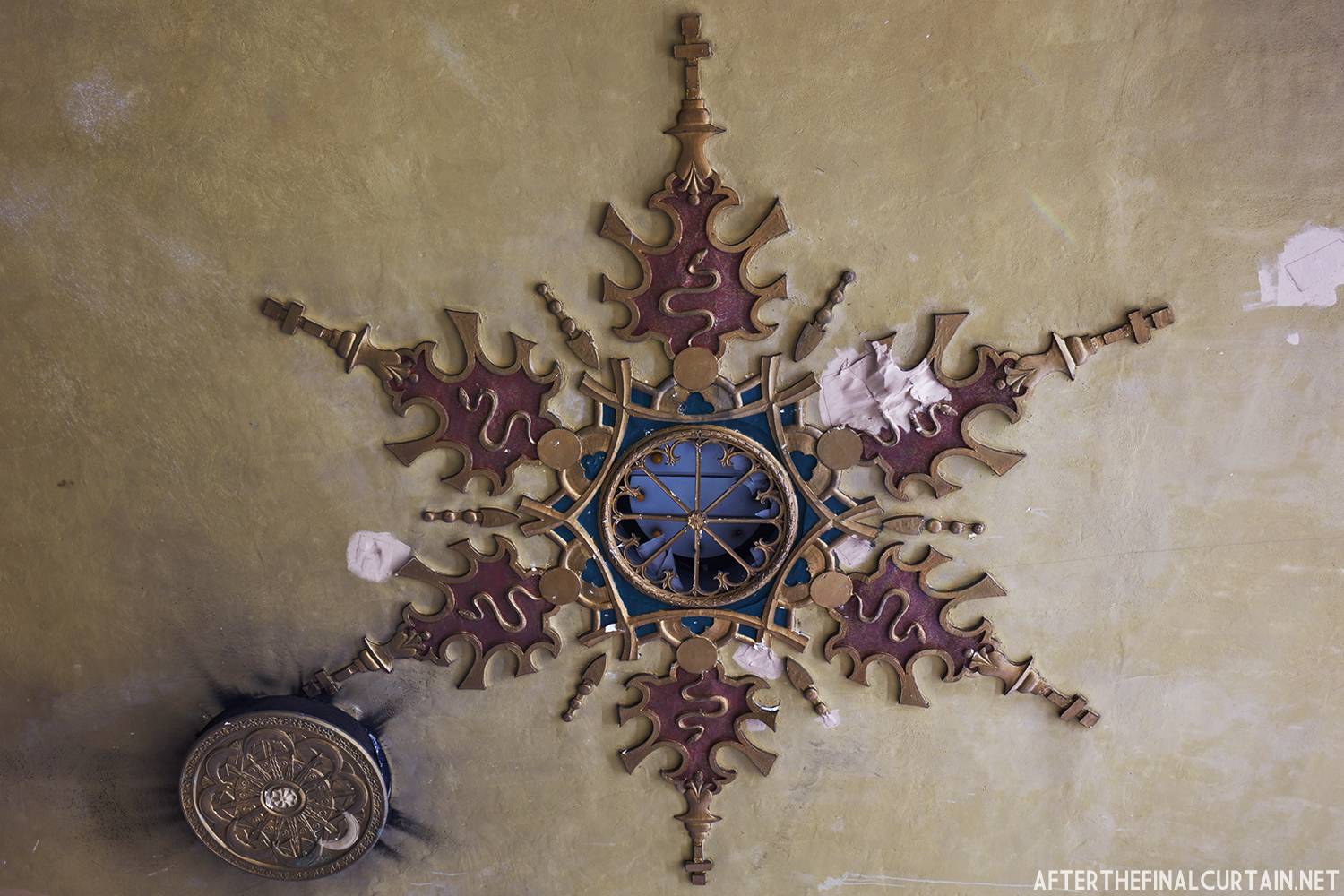
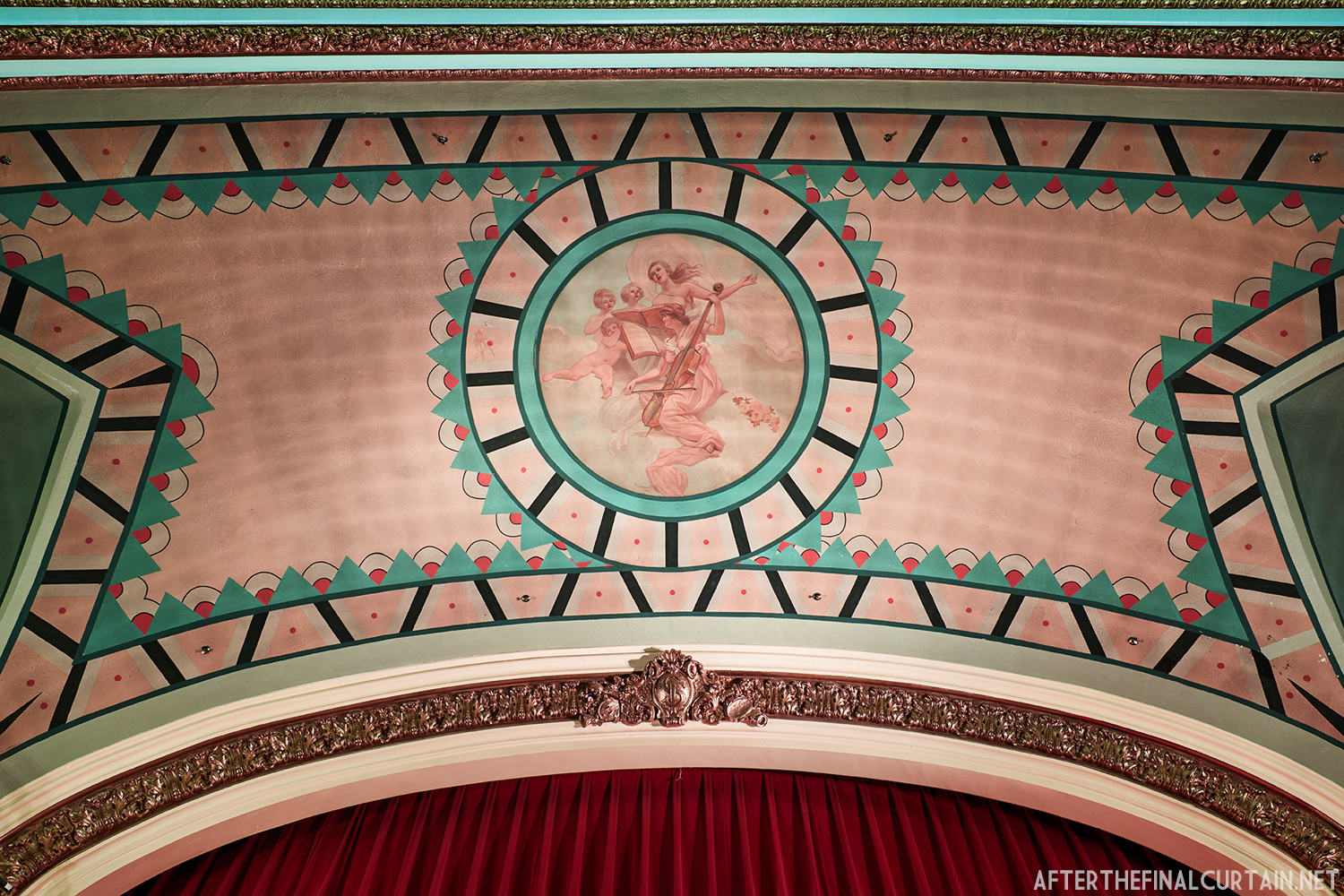
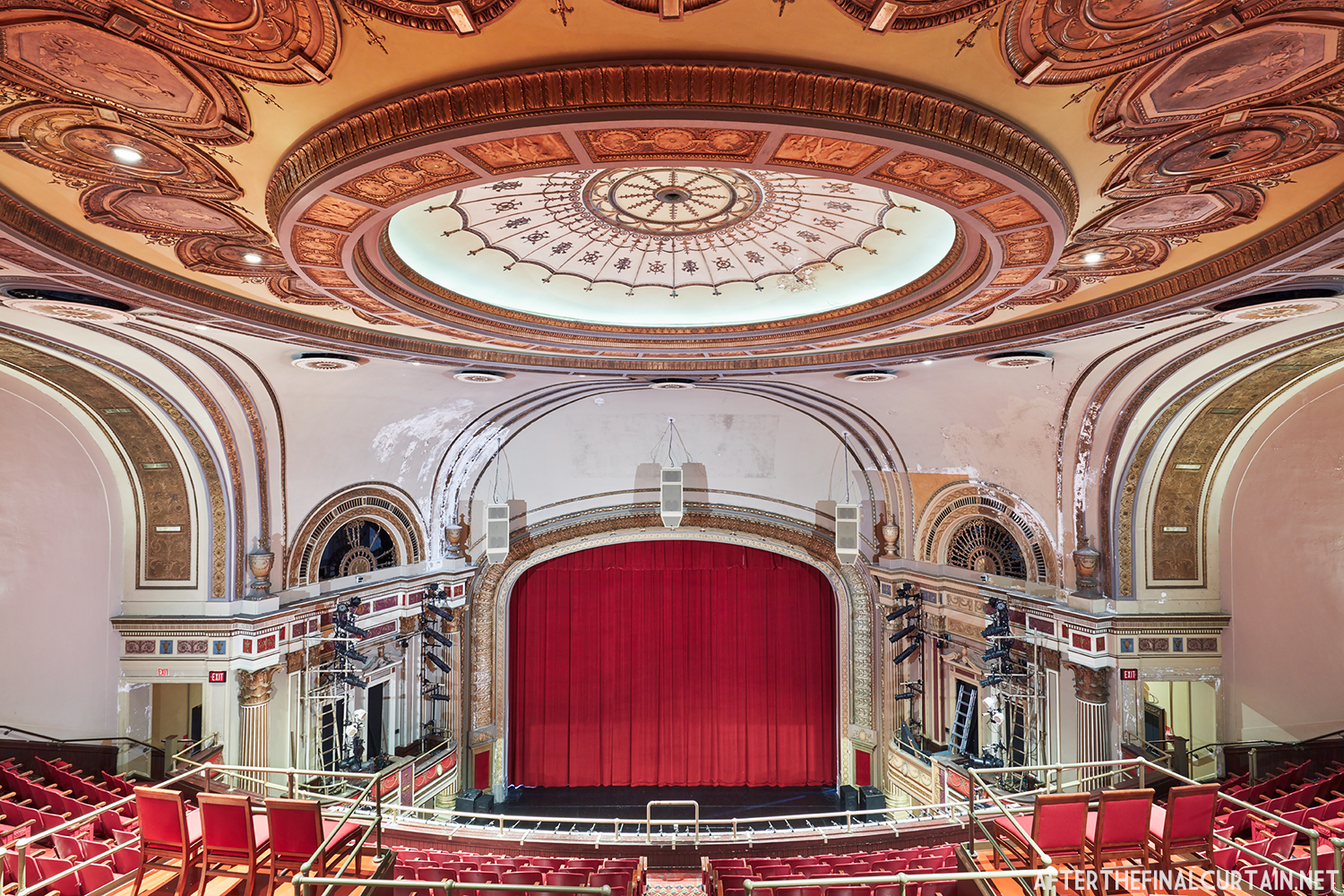
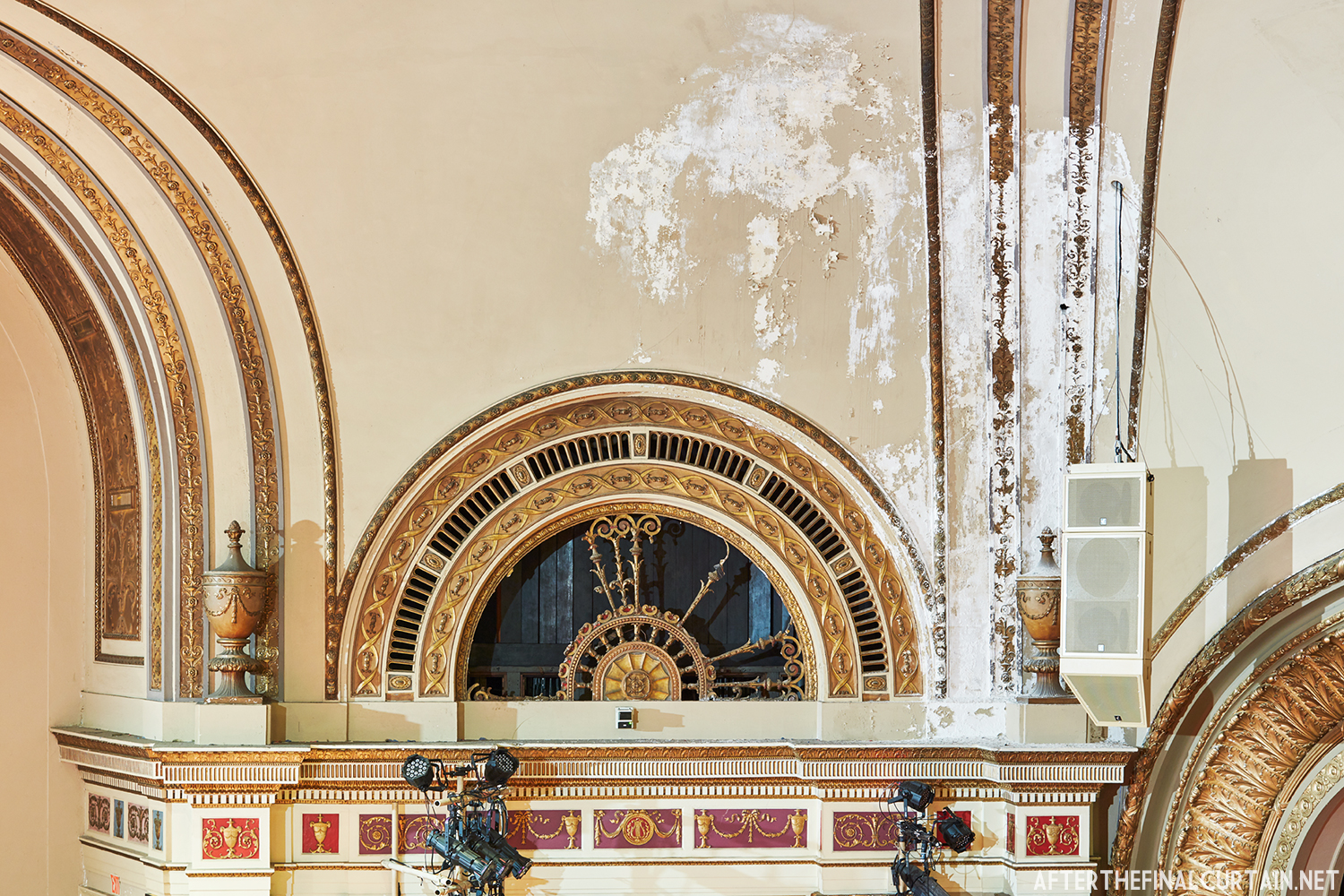
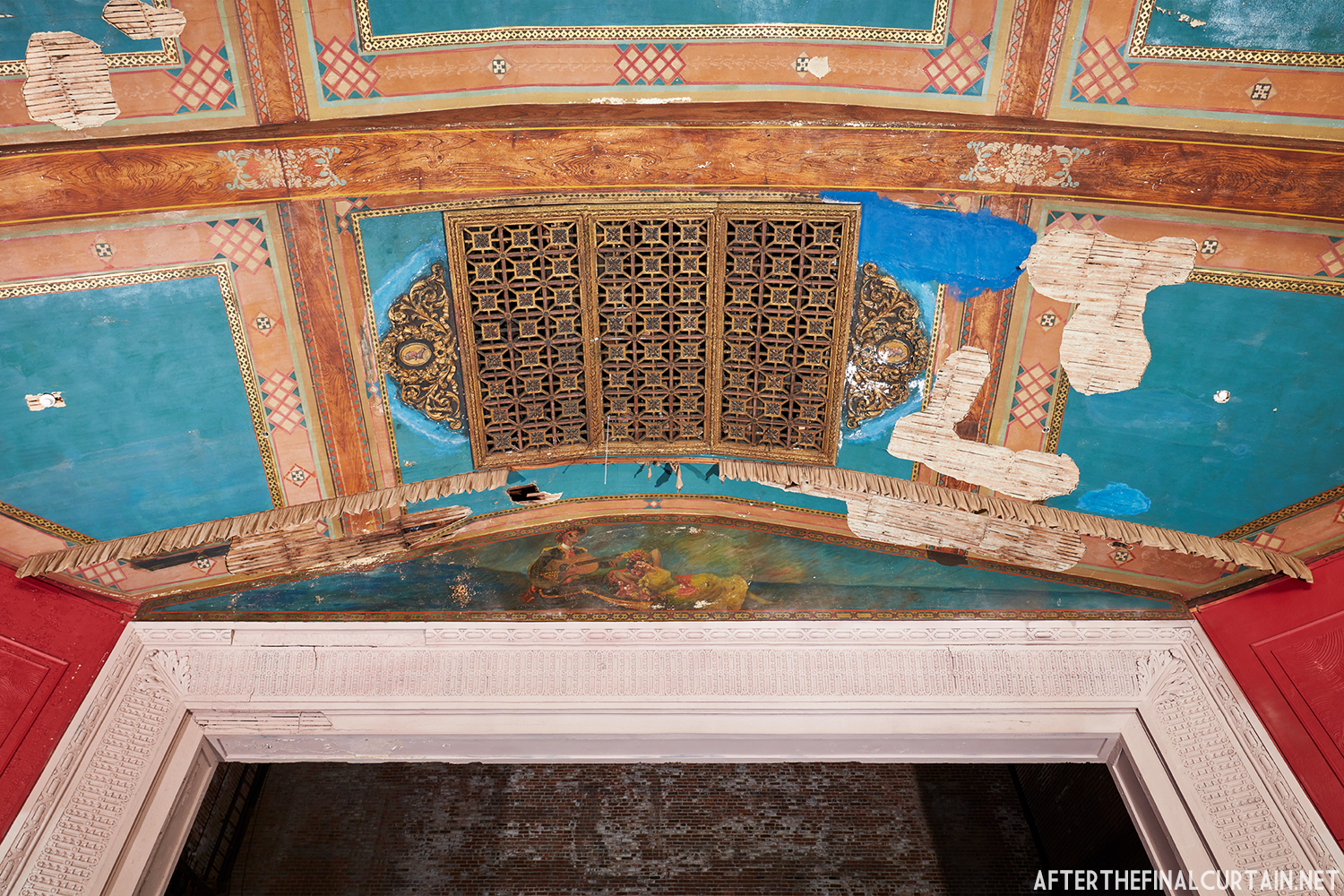
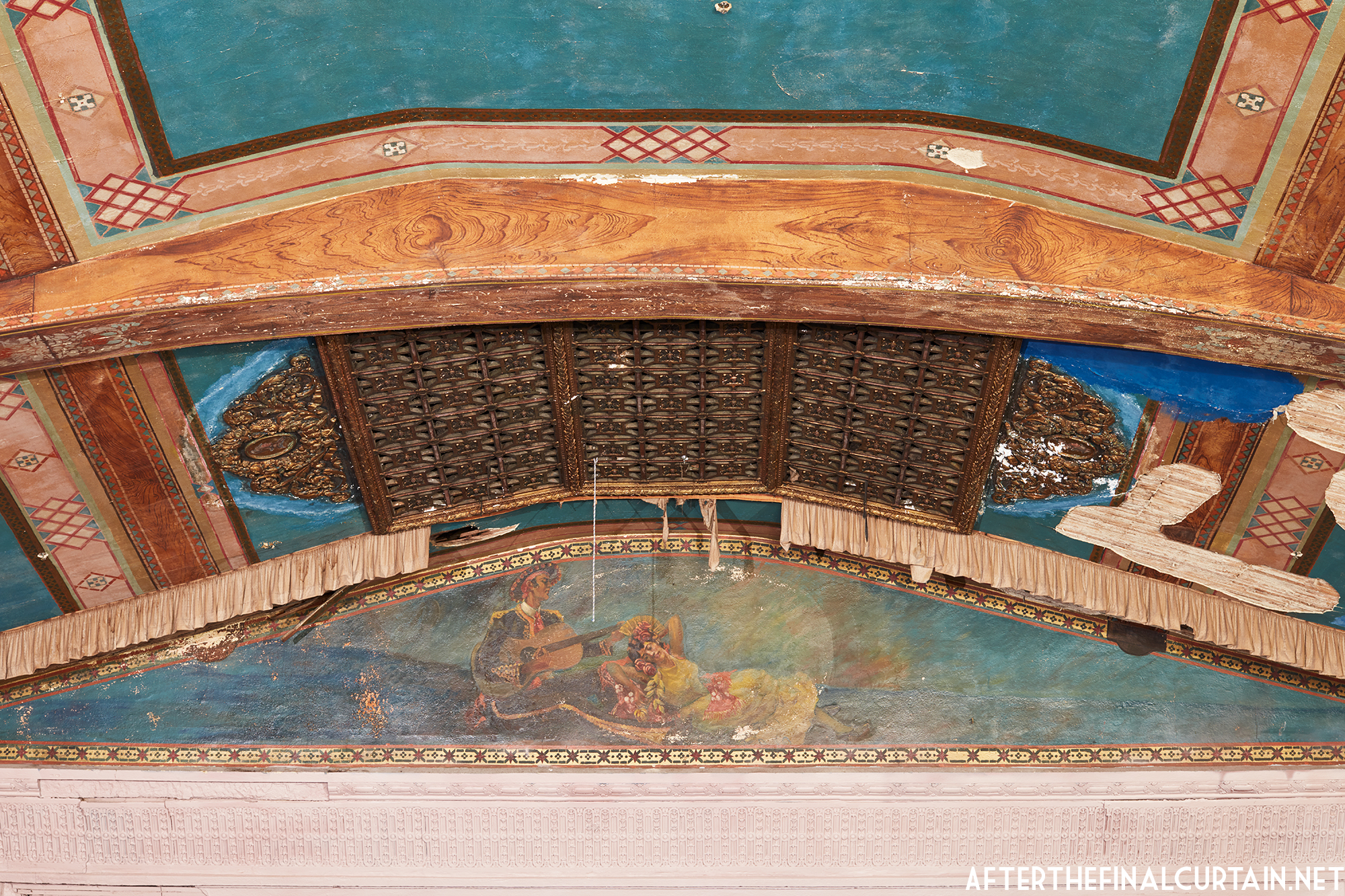
The Kurtz closed in July 1924 and the following month the building was purchased by the Wilmer & Vincent theater circuit and reopened as the Colonial Theatre. It was named after the Colonial Theatre in Allentown, PA, which they also owned. In 1925, the interior of the theater was remodeled to the plans of William H. Lee, who also designed the Boyd Theatre in Philadelphia, PA and the Drake Theatre in Oil City, PA.
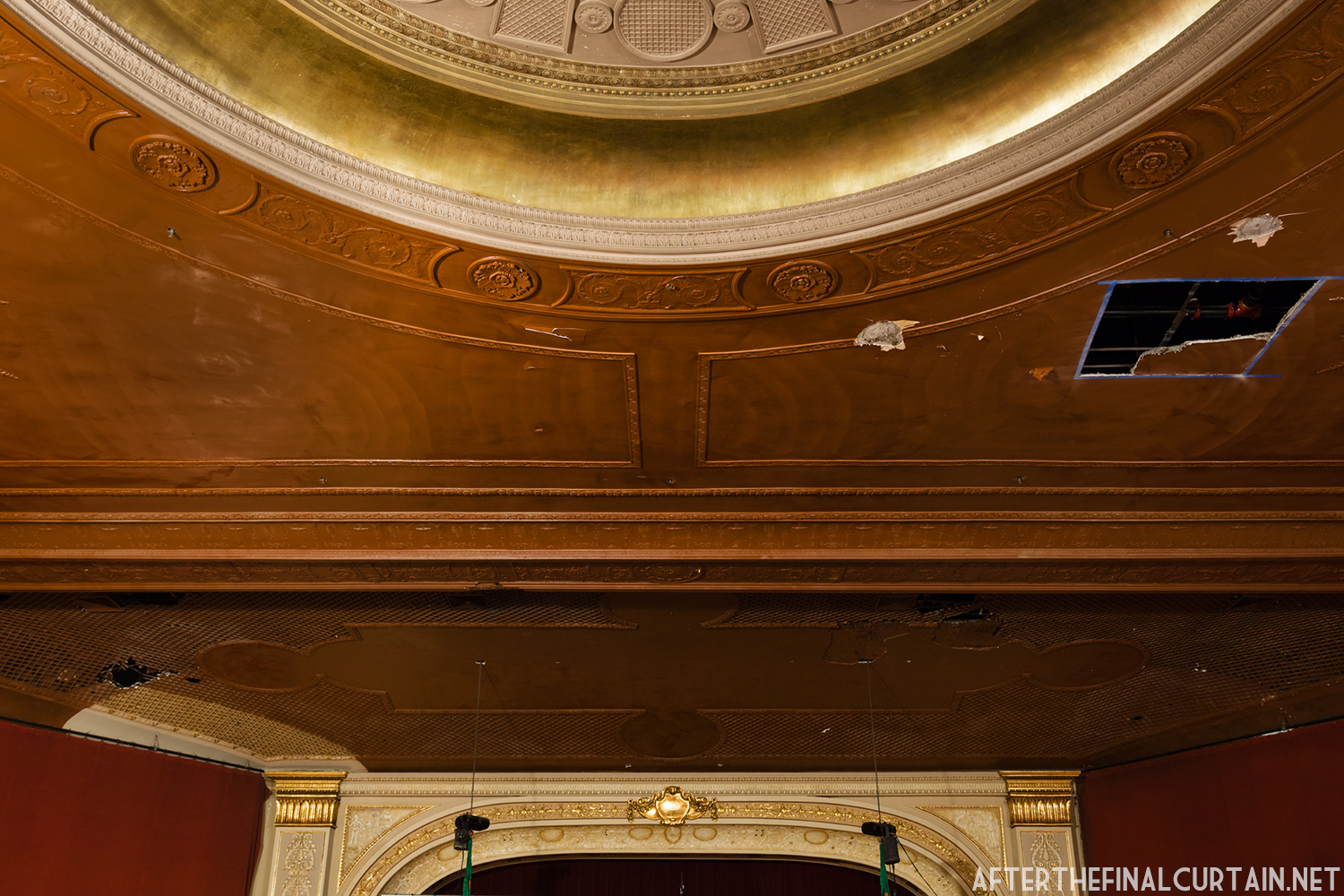
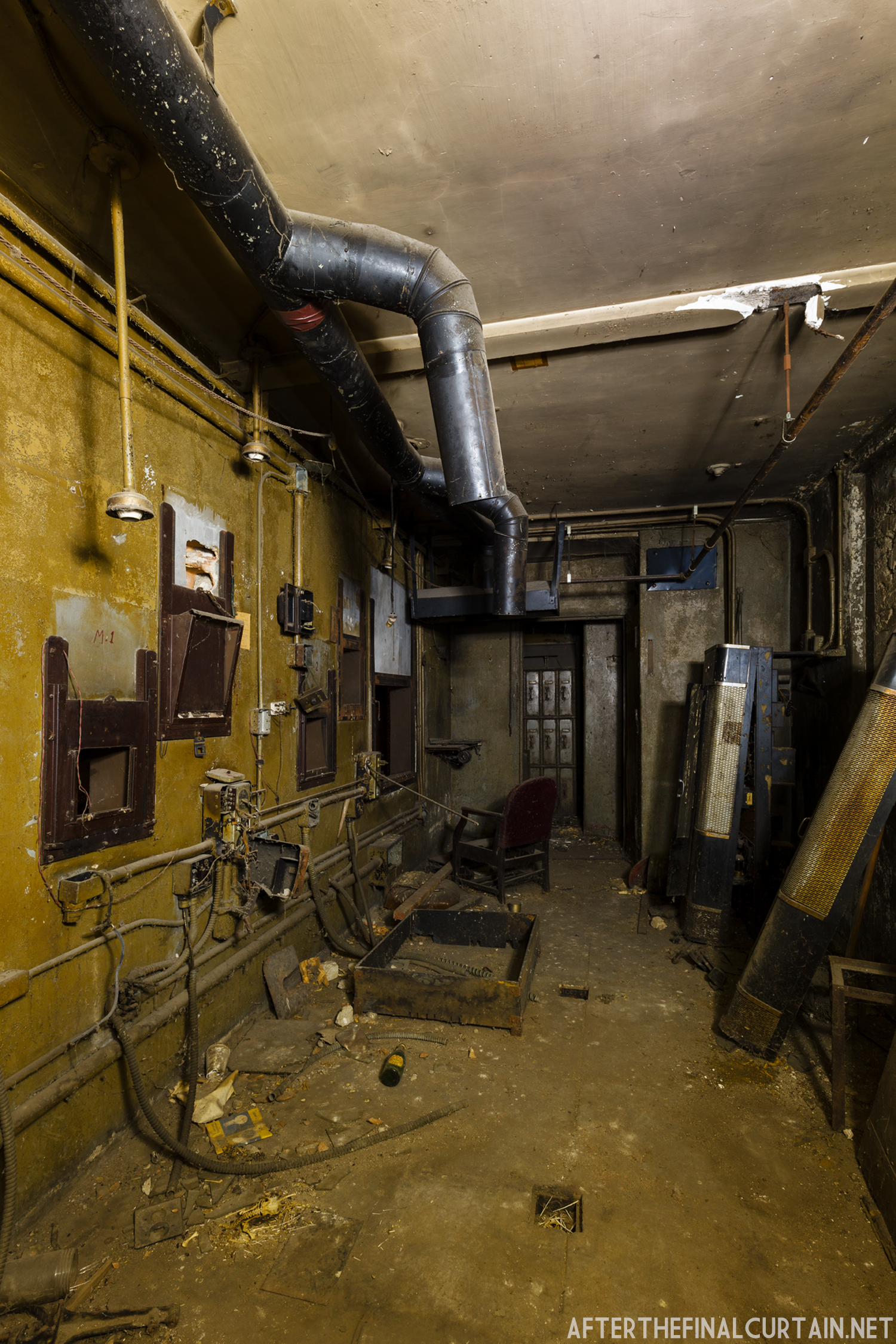
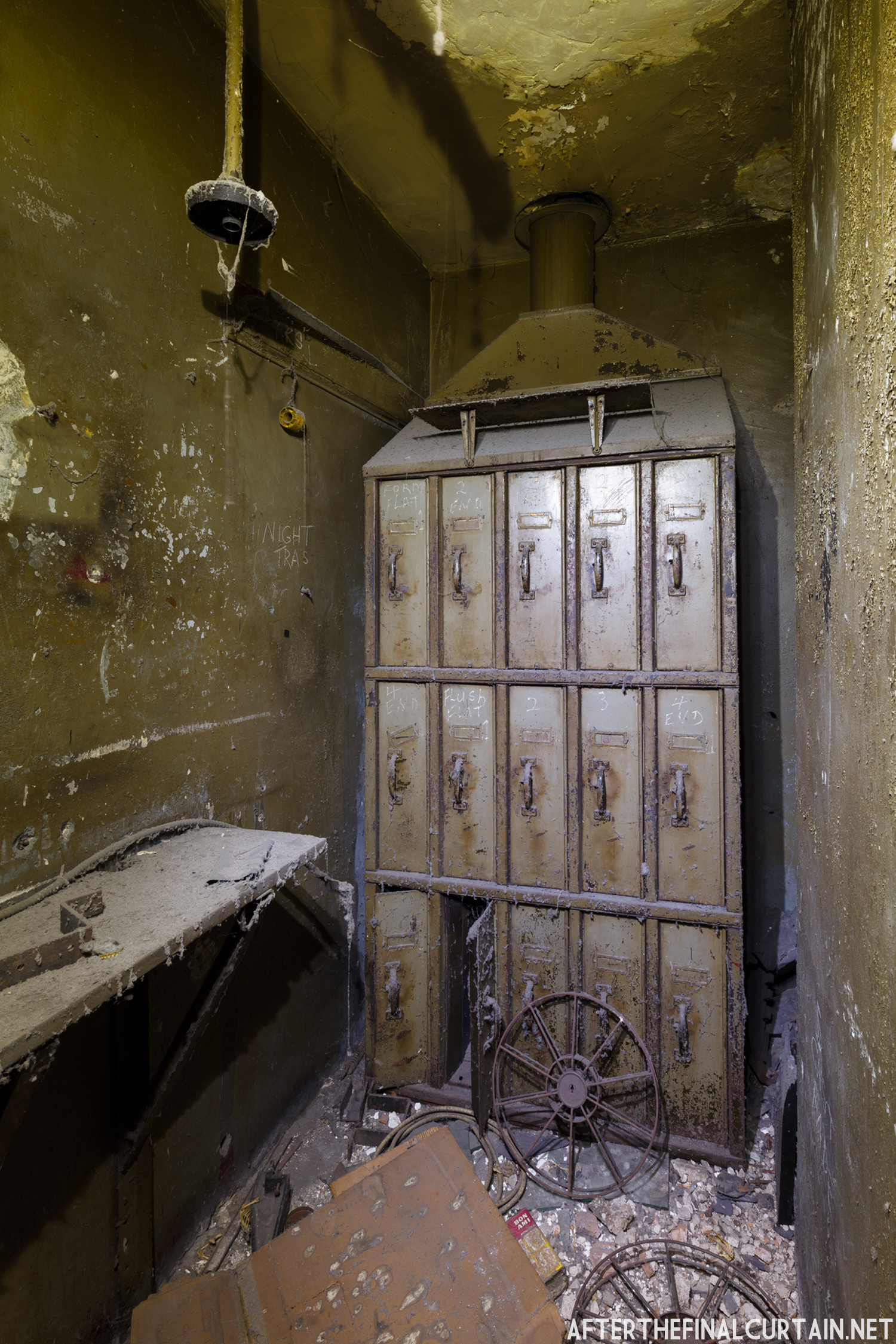
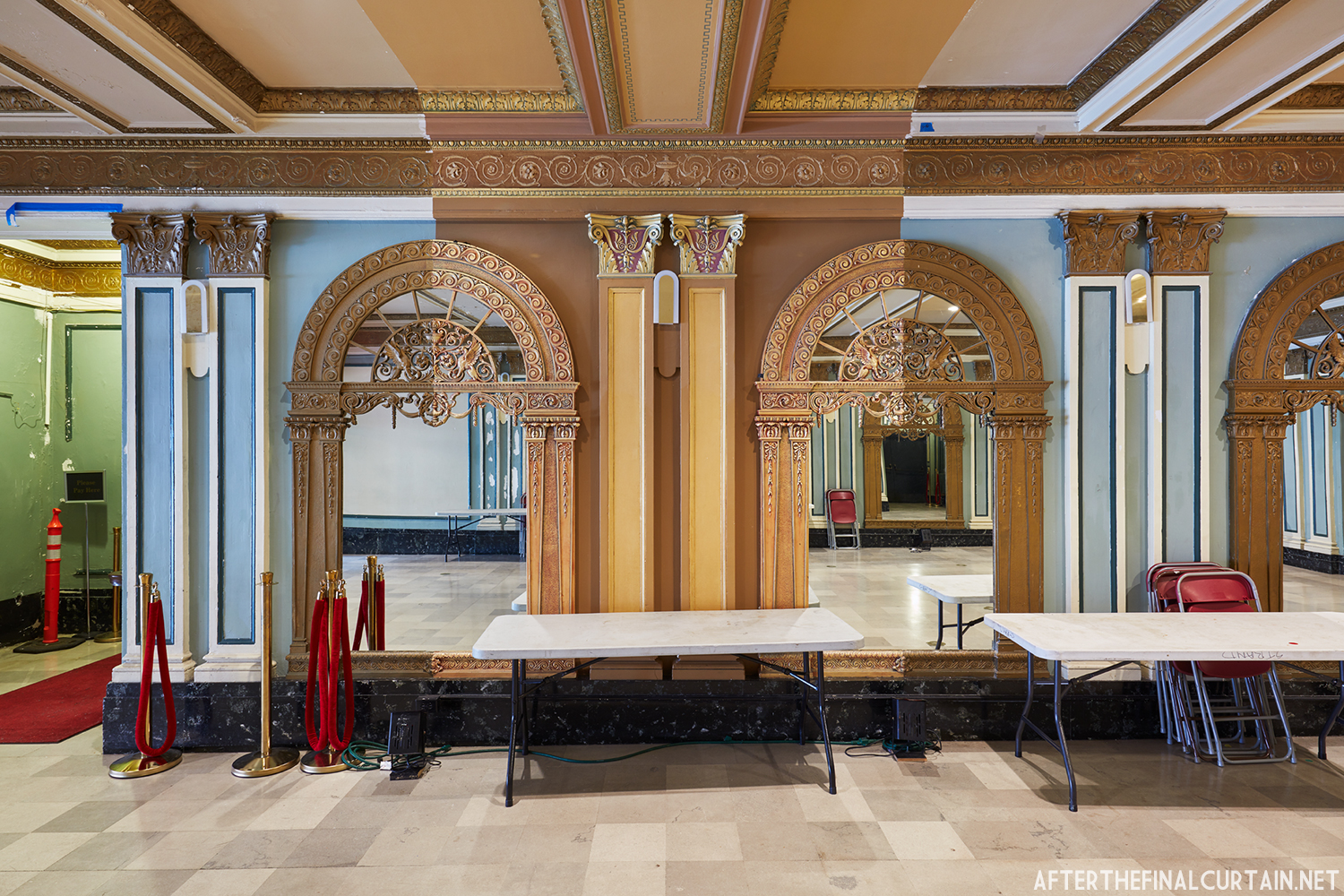
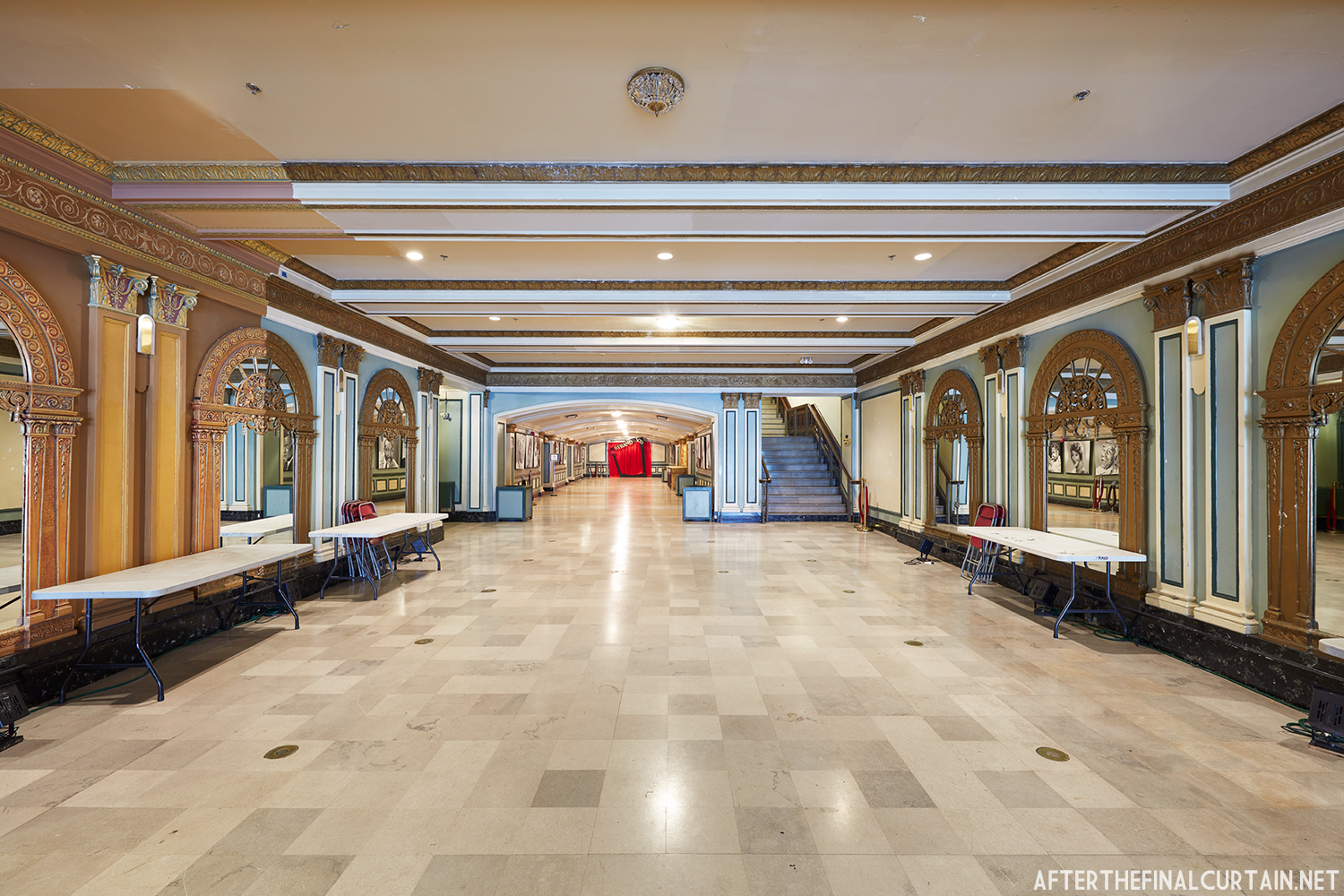
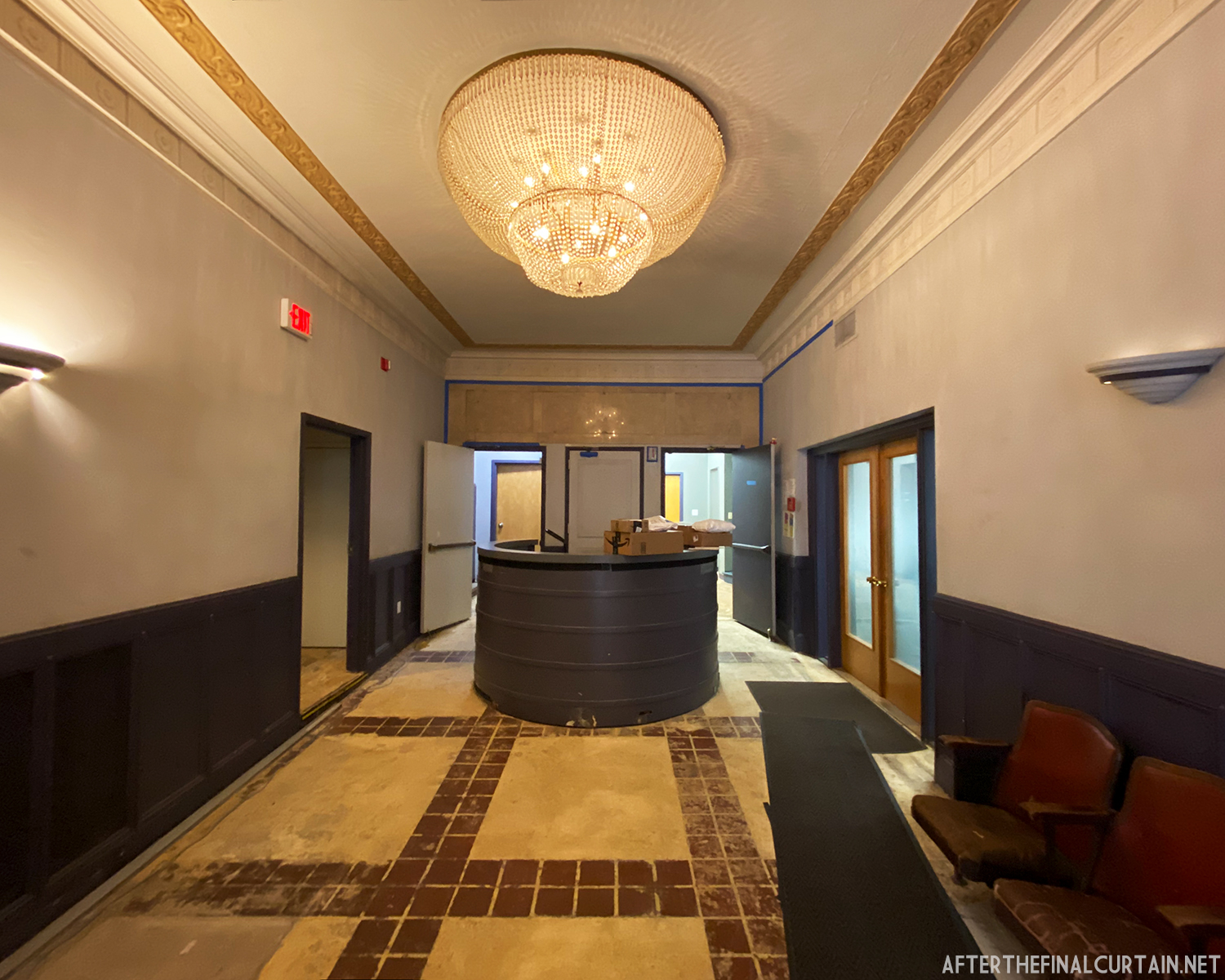
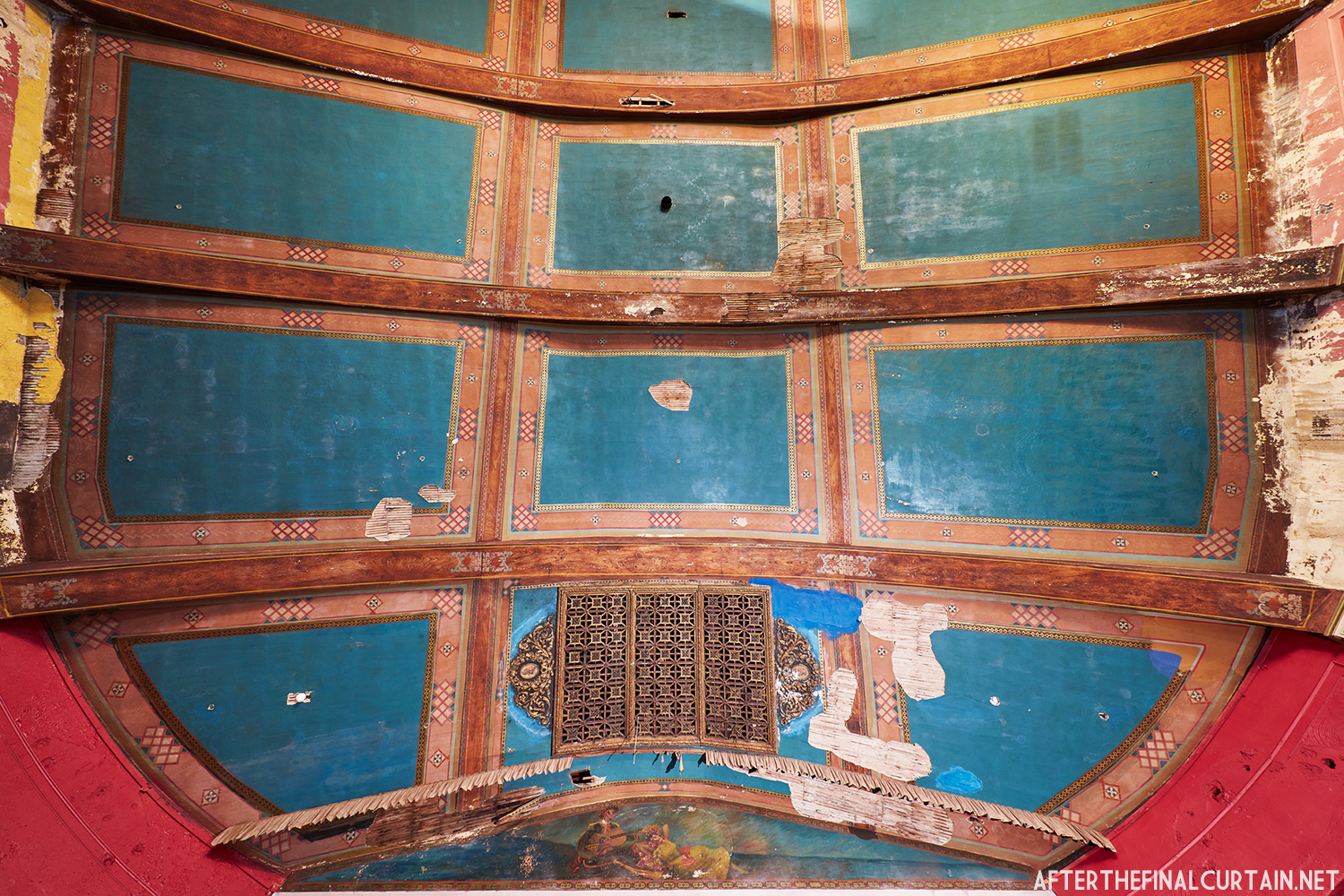
In 1934, the building was purchased by A.R. Boyd Enterprises of Philadelphia, and renamed the Boyd Theatre. A.R. Boyd Enterprises also operated the Boyd Theaters in Philadelphia, Allentown and Easton, PA. On December 27, 1966, a fire broke out at the theater. The fire destroyed much of the Boyd’s lobby and some of the retail spaces in the front of the building. Bethlehem’s building inspector condemned the remains of the lobby, and it had to be completely rebuilt, which kept the theater from reopening until early 1968.
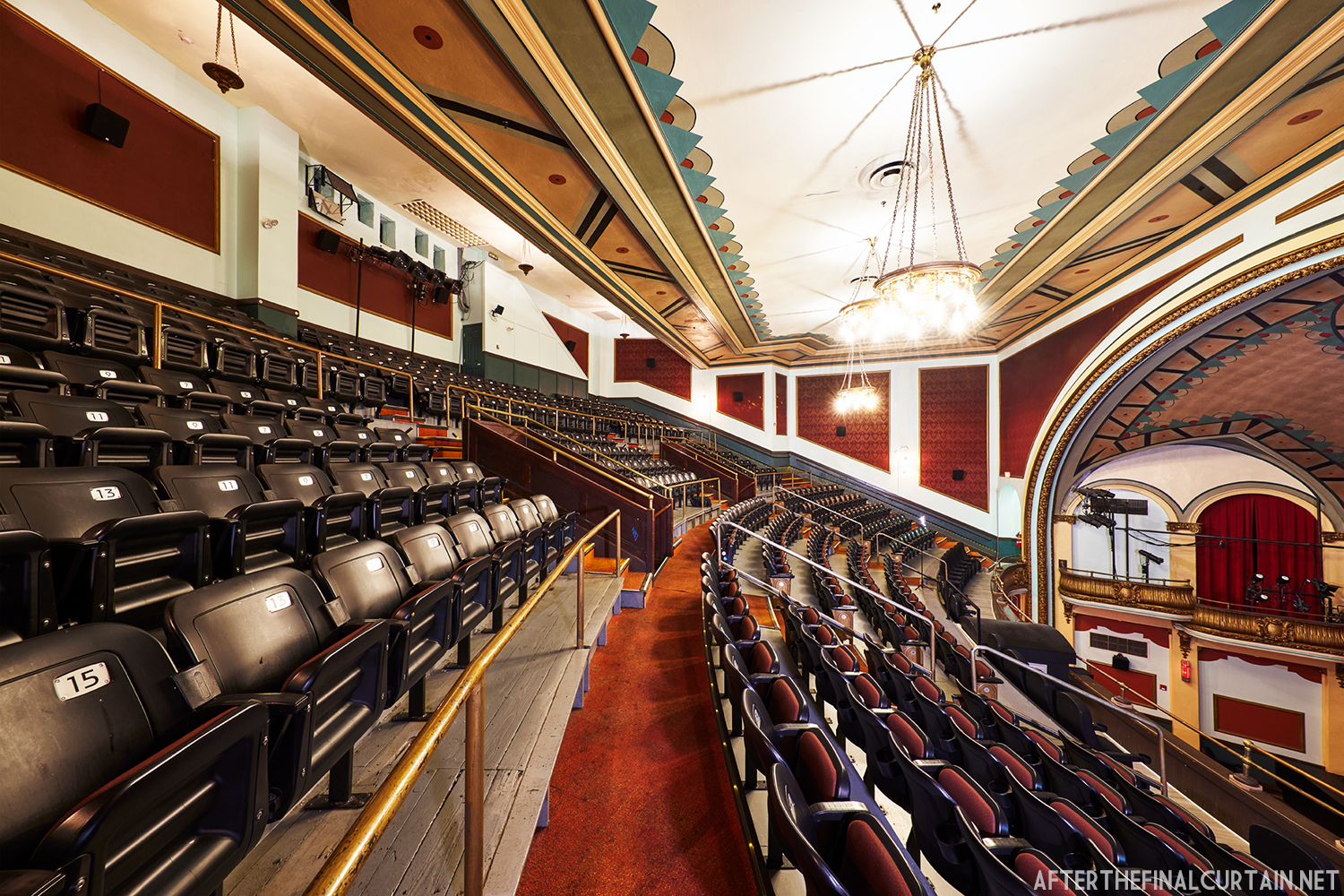
The Boyd was sold to a local family in 1970, and they continued to operate it as a single screen theater. However, the balcony was closed more often than not. A new Dolby Digital Surround sound system was installed in 1999 and was used for the first time during a showing of “Star Wars Episode I – The Phantom Menace.”
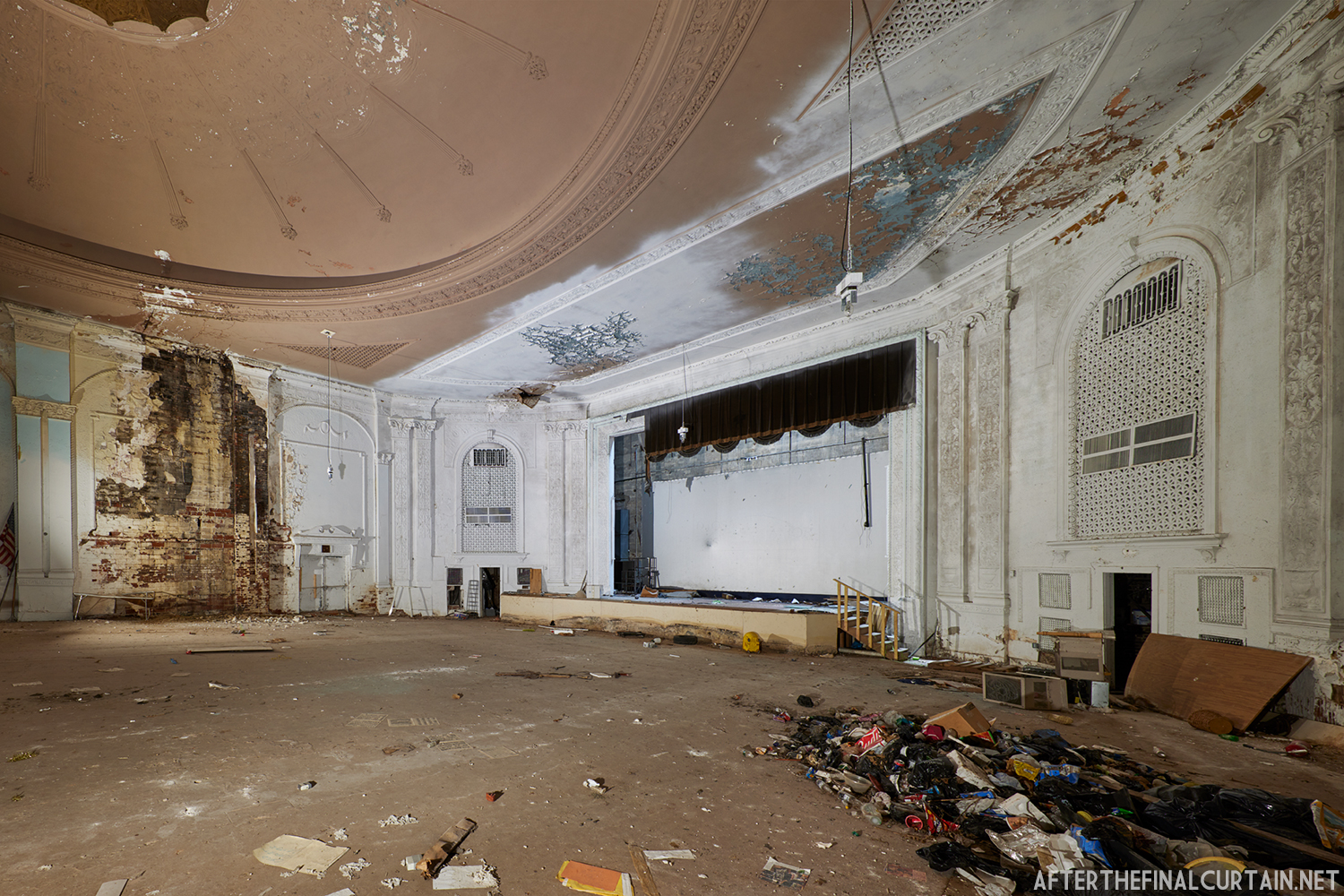
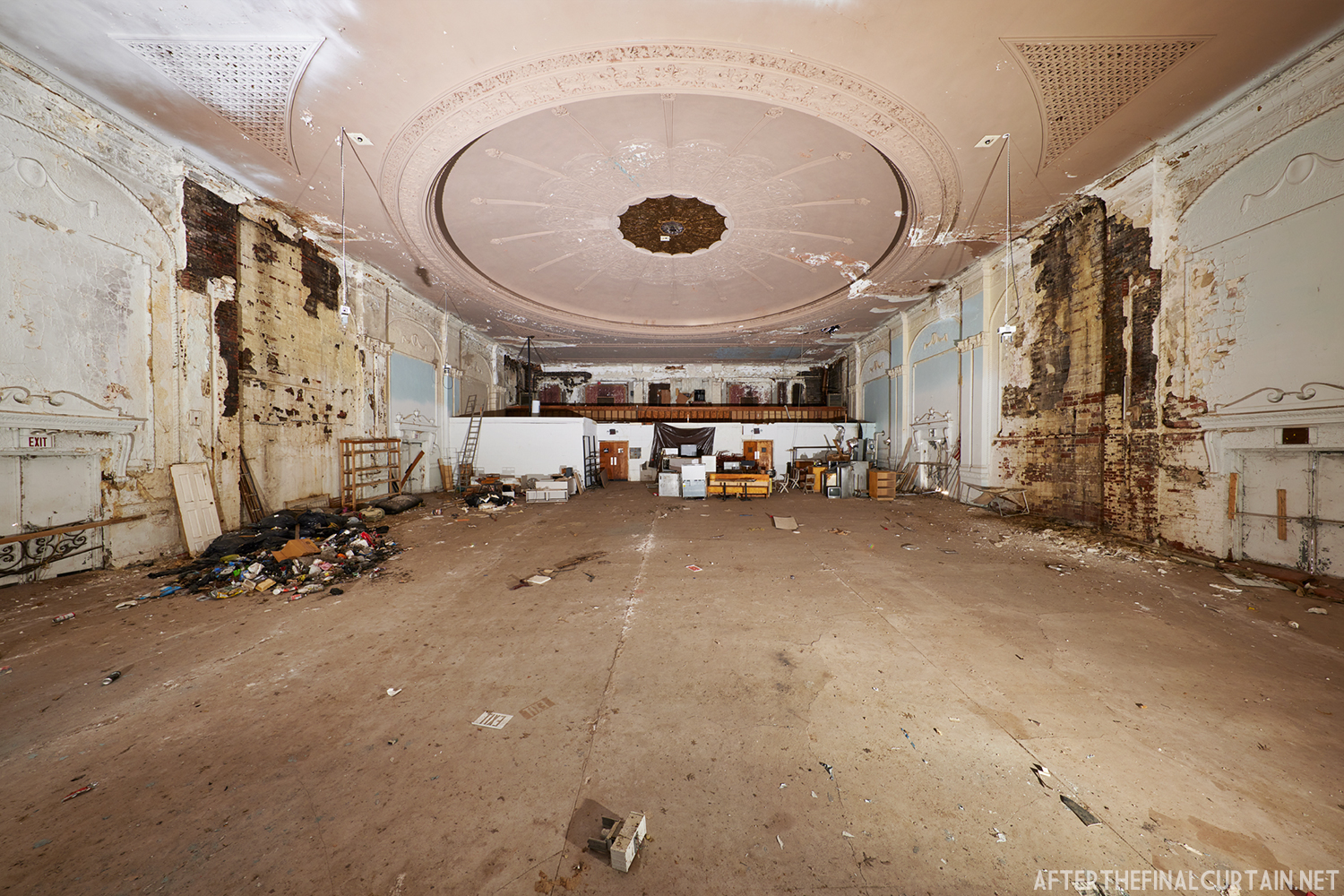
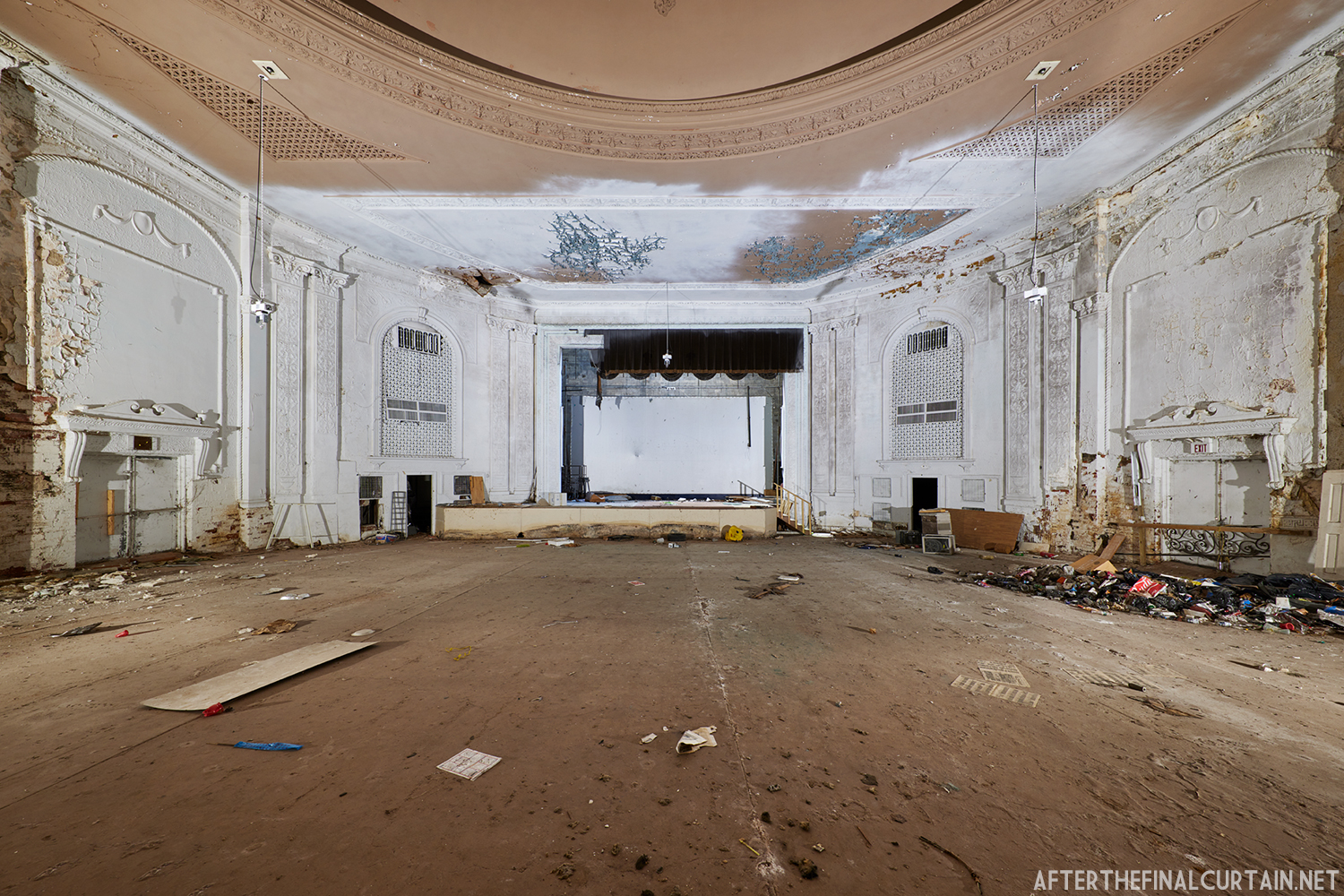
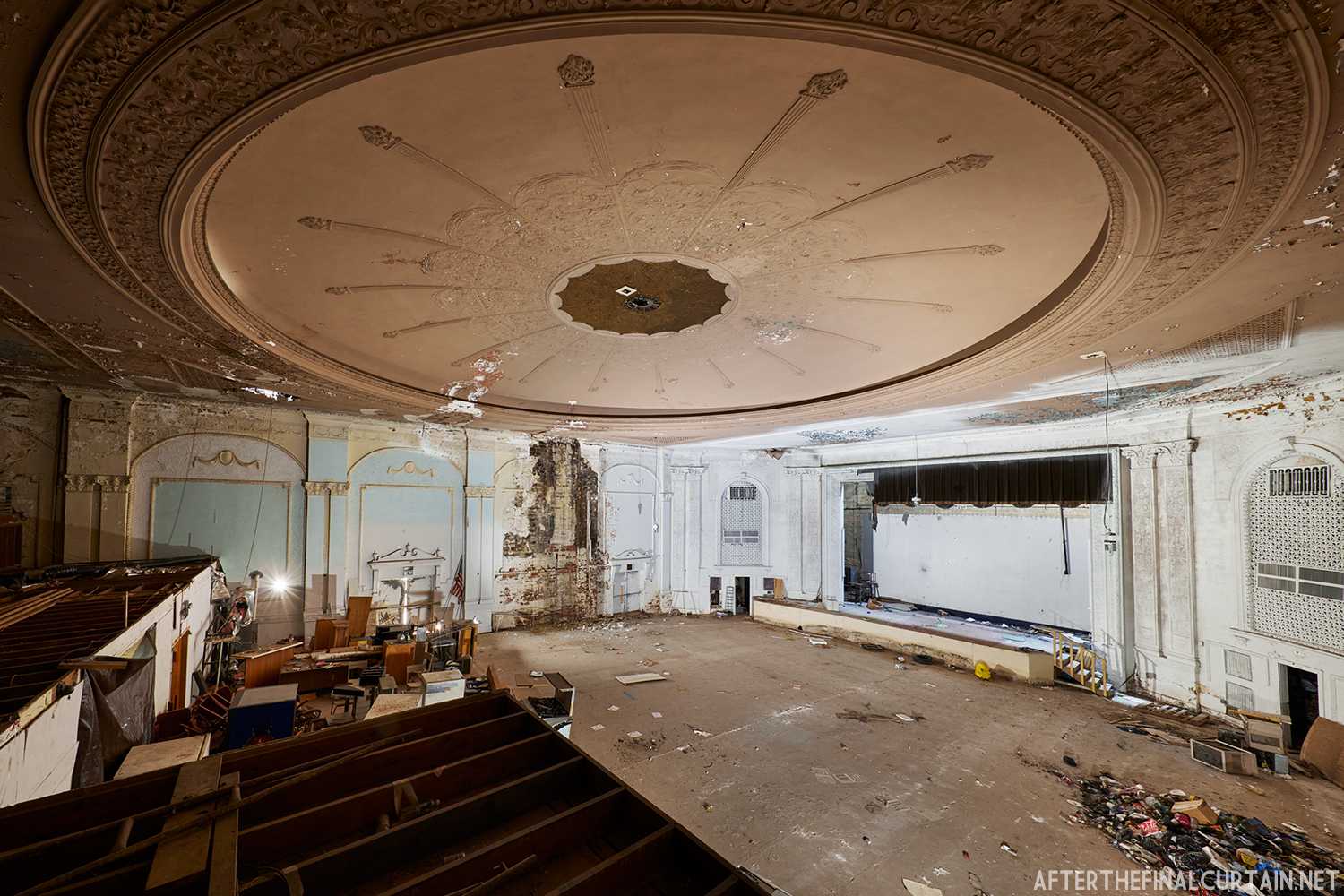
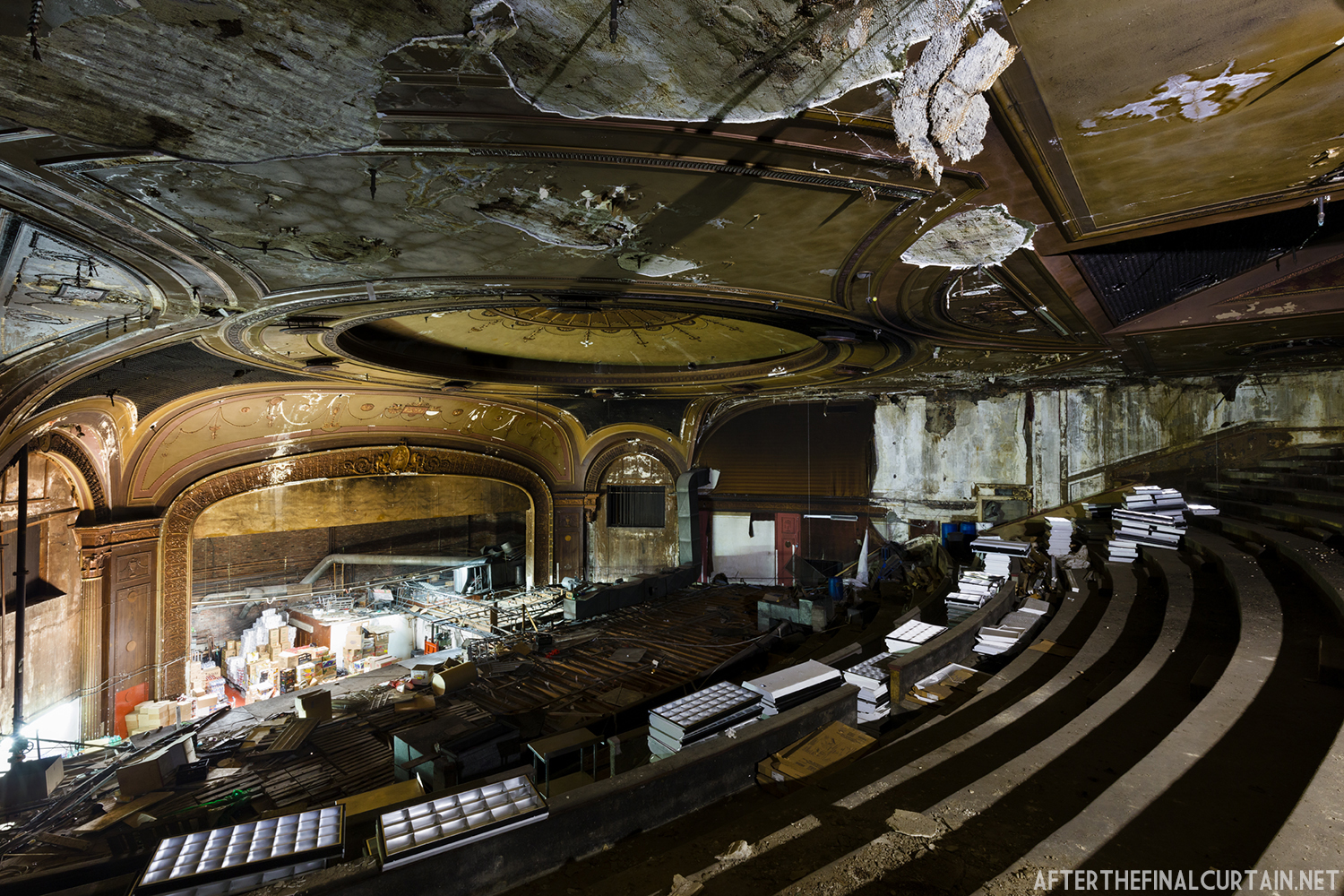
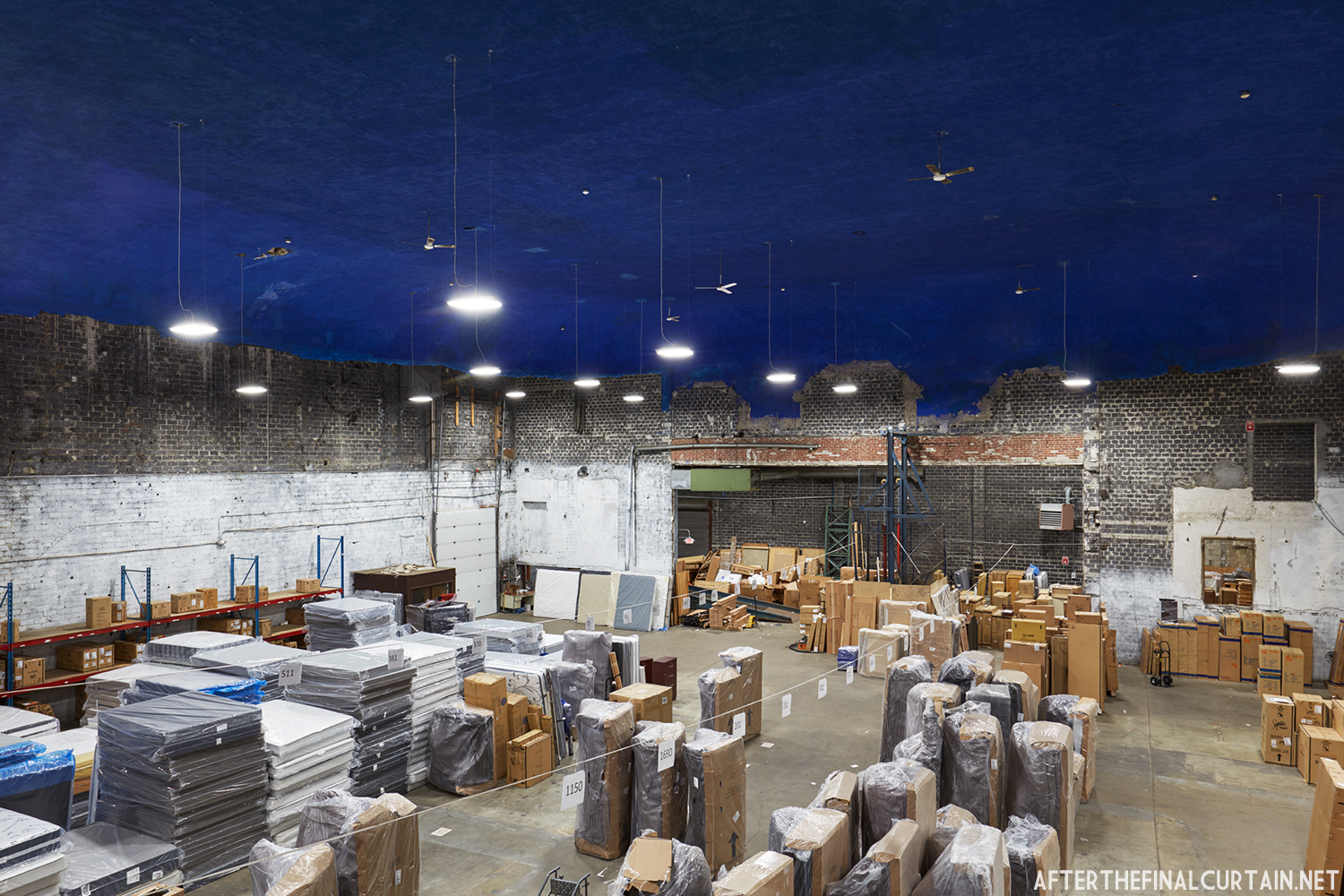
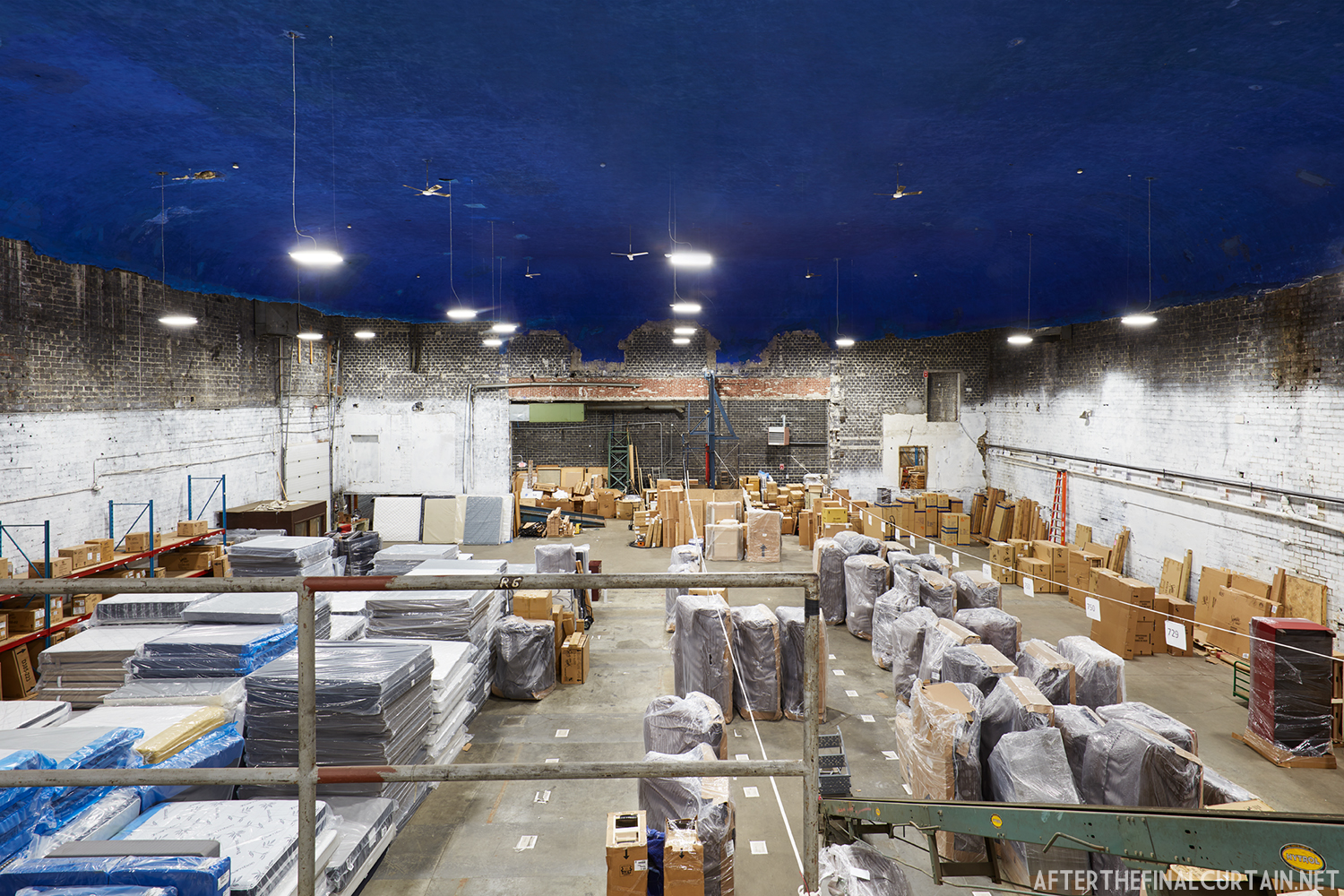
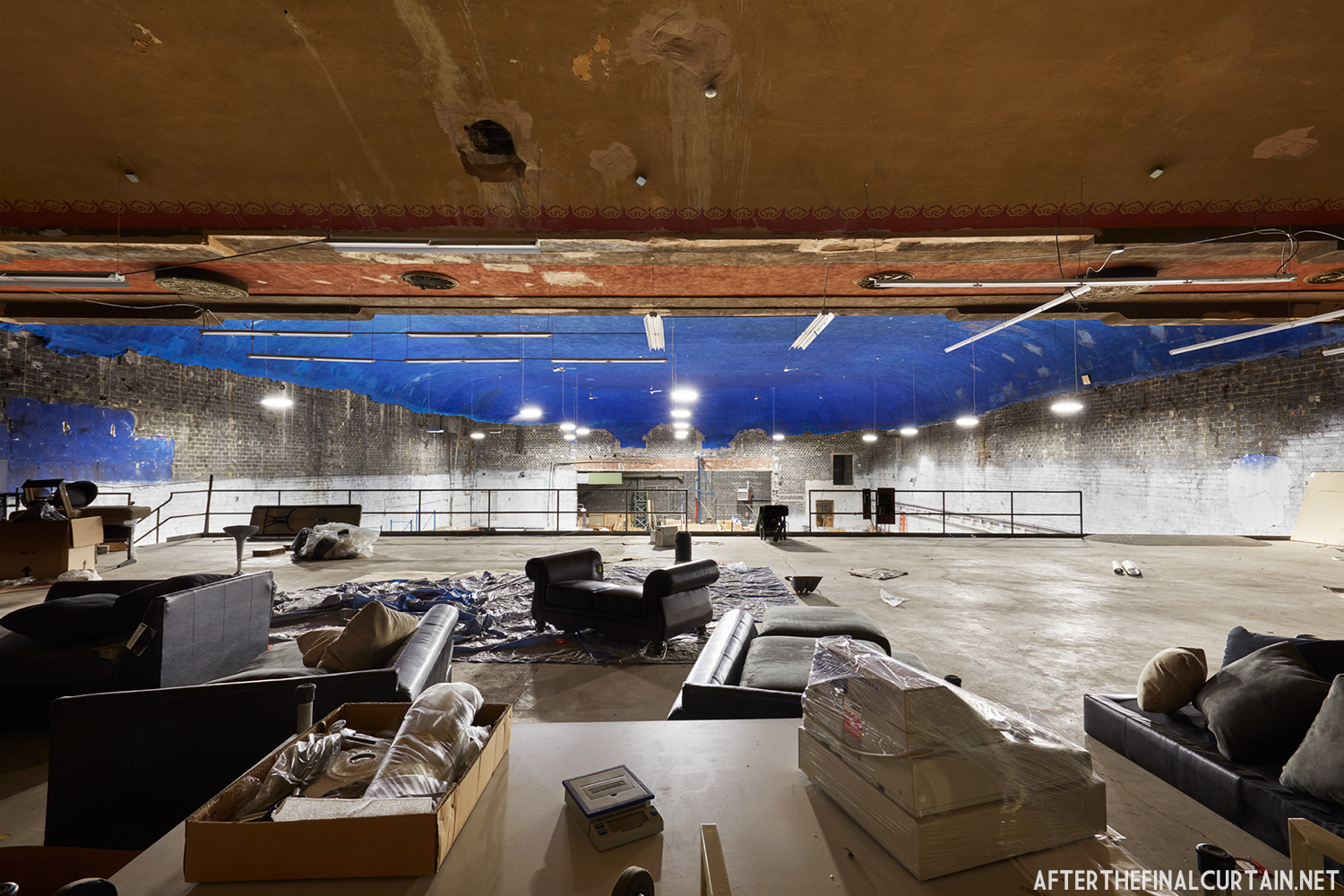
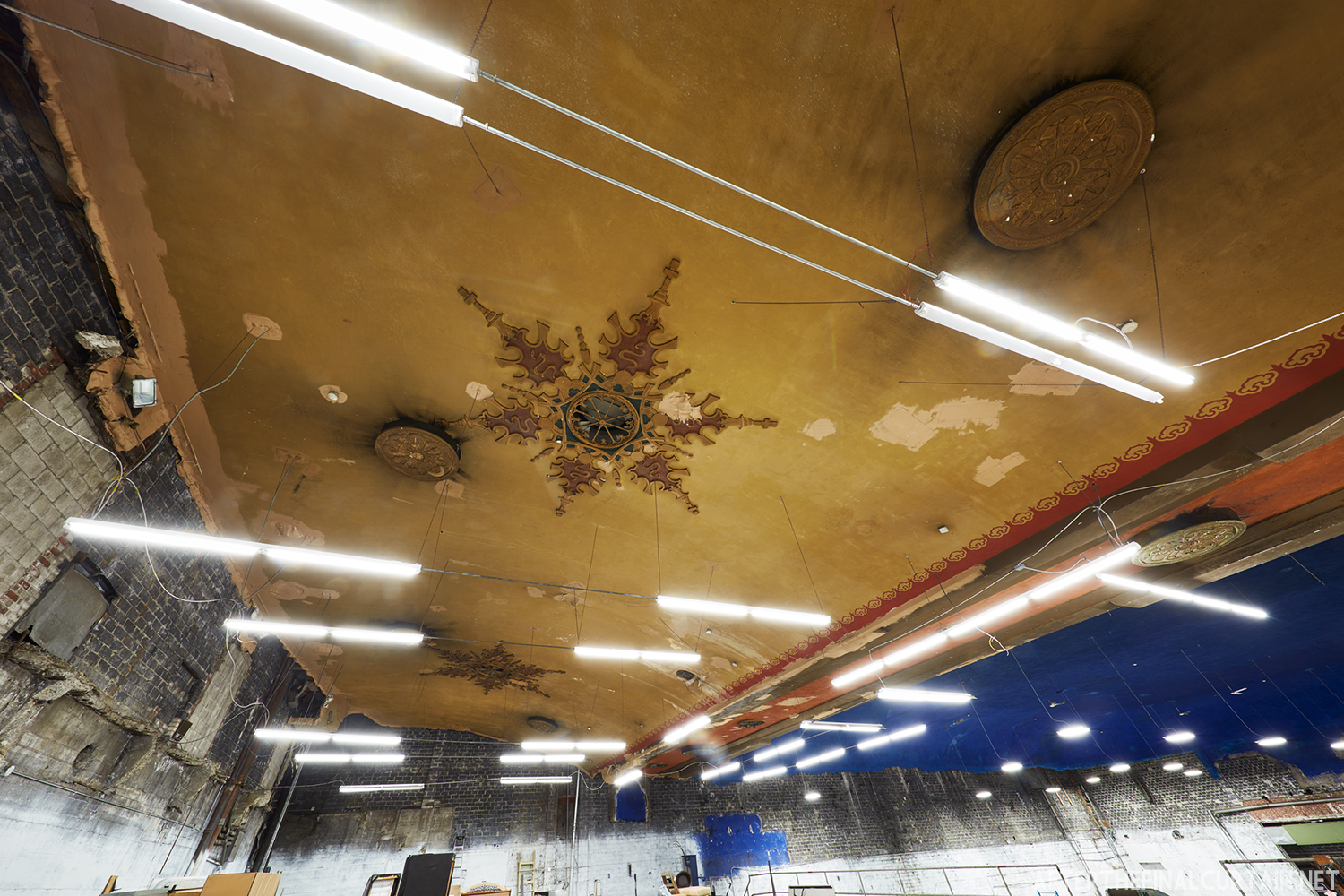
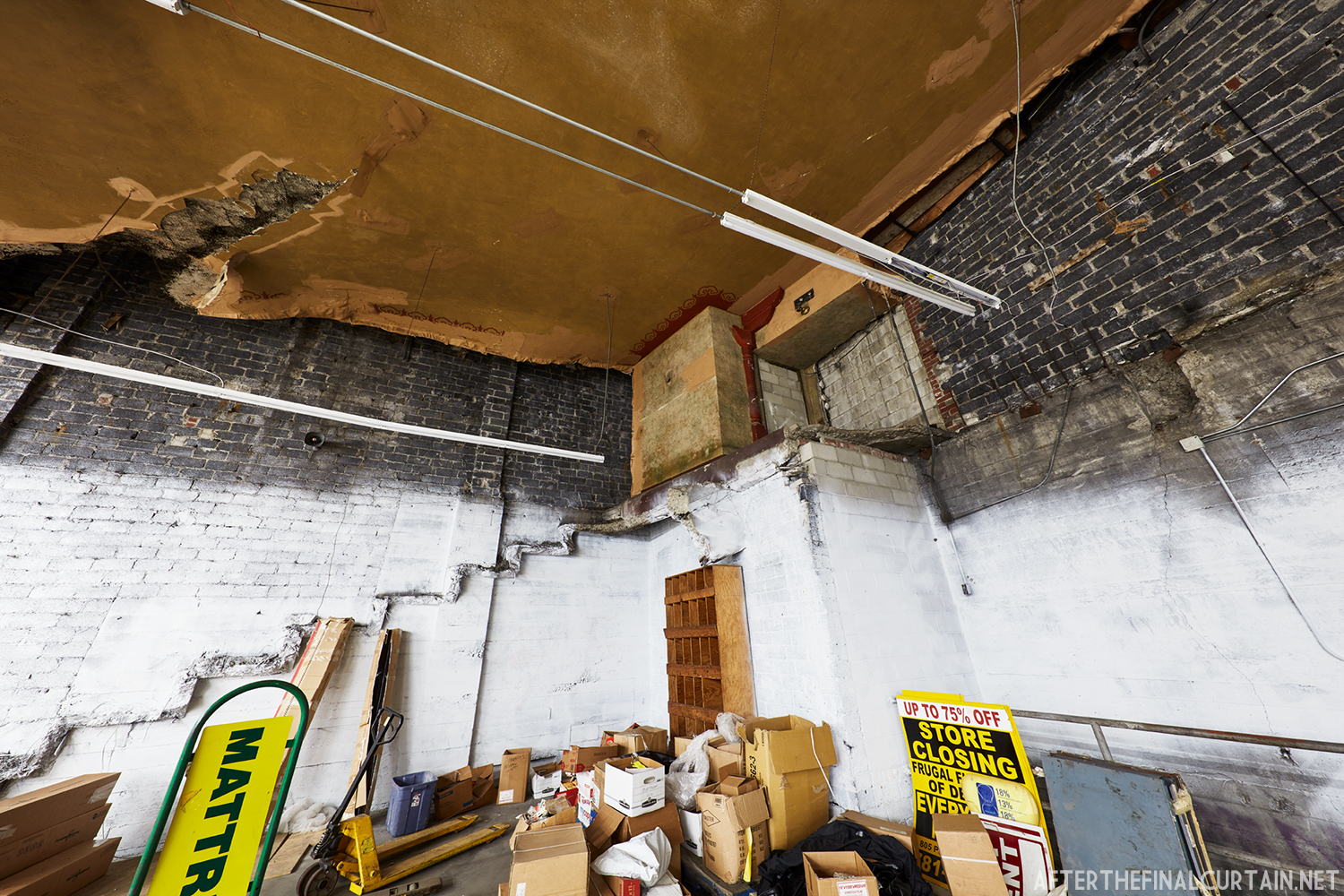
The Boyd was damaged by heavy rainstorms in May 2011, and the owners announced it would be closed for the rest of the year while repairs were made. Unfortunately, the theater continued to deteriorate, never reopened, and was eventually sold. In February 2019, it was announced that the Boyd would be demolished and replaced by a 13 story apartment building. The theater was sold again in early 2021 to DLP Real Estate Capital and Monocacy General Contracting, and the replacement building was changed to six stories at a cost of $50 million.
Demolition began in February 2022, and was completed by early May. The “Boyd Theatre” sign was removed prior to the demolition and is planned to be incorporated into one of the new buildings’ courtyards. The new building is scheduled to be completed by 2023.